Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

5-Aminosalicylic Acid (5-ASA) is an anti-inflammatory agent, structurally related to the SALICYLATES, which is active in INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE. It is considered to be the active moiety of SULPHASALAZINE.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $45 | In Stock |
| Description | 5-Aminosalicylic Acid (5-ASA) is an anti-inflammatory agent, structurally related to the SALICYLATES, which is active in INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE. It is considered to be the active moiety of SULPHASALAZINE. |
| In vivo | At 2 mM, Mesalamine or sulfasalazine significantly reduces the expression of TC22 transcript and reversibly inhibits the expression of TC22 protein in a dose-dependent manner. Mesalamine induces the membrane expression of E-cadherin protein, enhancing intercellular adhesion. It also regulates the glycosylation of E-cadherin, elevating the mRNA and protein levels of GnT-III. In the range of 0.1-1 mM, Mesalamine dose-dependently suppresses chemiluminescence mediated by peroxynitrite, suggesting its ability to directly scavenge peroxynitrite. Only at a higher concentration, 1 mM, does Mesalamine inhibit both the hydroxyl radical adduct formation and the concurrent movement in electron paramagnetic resonance spectra. It inhibits 3-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase involved in the reversible conversion between DHP and THP, potentially affecting the local effects of DHP and THP in the brain. Furthermore, Mesalamine suppresses the phosphorylation of RelA triggered by IL-1. |
| Alias | Mesalazine, Mesalamine, 5-ASA |
| Molecular Weight | 153.14 |
| Formula | C7H7NO3 |
| Cas No. | 89-57-6 |
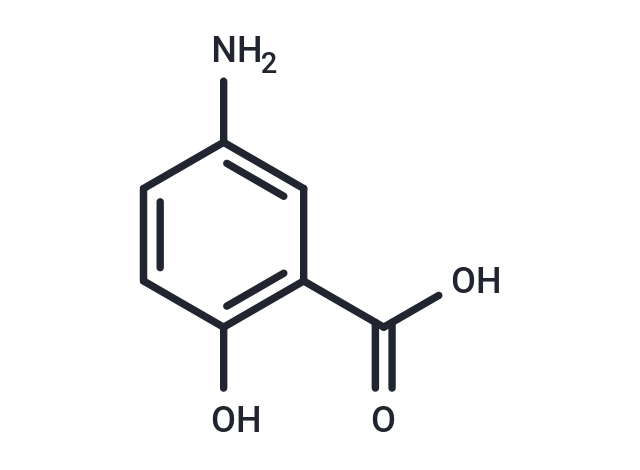
| Smiles | NC1=CC(C(O)=O)=C(O)C=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.3585 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 29 mg/mL (189.37 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 60 mg/mL (391.8 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.