Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

BX430 is used for chronic pain and cardiovascular disease and it is a potent and selective noncompetitive allosteric human P2X4 receptor channels antagonist with an IC50 of 0.54 μM. BX430 has species specificity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $38 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $68 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $143 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $230 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $341 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $488 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $42 | In Stock |
| Description | BX430 is used for chronic pain and cardiovascular disease and it is a potent and selective noncompetitive allosteric human P2X4 receptor channels antagonist with an IC50 of 0.54 μM. BX430 has species specificity. |
| Targets&IC50 | P2X4 receptor (human):0.54 μM |
| In vitro | BX430, with submicromolar potency (IC50 = 0.54 M). BX430 is highly selective, having virtually no functional impact on all other P2X subtypes, namely, P2X1-P2X3, P2X5, and P2X7, at 10-100 times its IC50.?Unexpected species differences were noticed, as BX430 is a potent antagonist of zebrafish P2X4 but has no effect on rat and mouse P2X4 orthologs.?The concentration-response curve for ATP on human P2X4 in the presence of BX430 shows an insurmountable blockade, indicating a noncompetitive allosteric mechanism of action.?Using a fluorescent dye uptake assay, we observed that BX430 also effectively suppresses ATP-evoked and ivermectin-potentiated membrane permeabilization induced by P2X4 pore dilation.?Finally, in single-cell calcium imaging, we validated its selective inhibitory effects on native P2X4 channels at the surface of human THP-1 cells that were differentiated into macrophages.?In summary, this ligand provides a novel molecular probe to assess the specific role of P2X4 in inflammatory and neuropathic conditions, where ATP signaling has been shown to be dysfunctional[1]. |
| Molecular Weight | 413.11 |
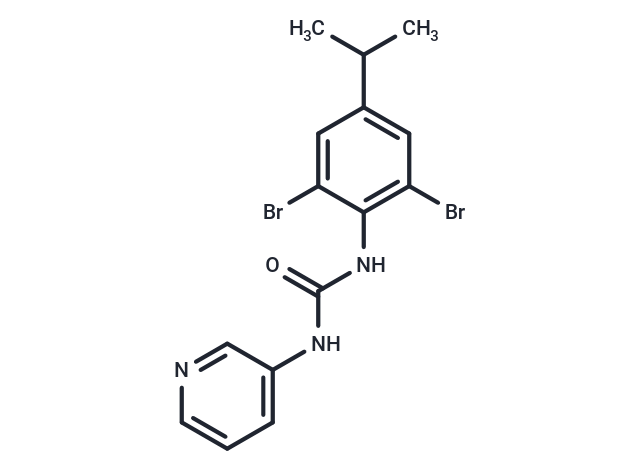
| Formula | C15H15Br2N3O |
| Cas No. | 688309-70-8 |
| Smiles | CC(C)c1cc(Br)c(NC(=O)Nc2cccnc2)c(Br)c1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 30 mg/mL (72.62 mM) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.