Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

CCCP (Carbonyl Cyanide m-Chlorophenylhydrazone) is an oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) inhibitor and mitochondrial proton carrier uncoupler. CCCP inhibits the activation of STING and its downstream signaling molecules TBK1 and IRF3.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $58 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $45 | In Stock |
| Description | CCCP (Carbonyl Cyanide m-Chlorophenylhydrazone) is an oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) inhibitor and mitochondrial proton carrier uncoupler. CCCP inhibits the activation of STING and its downstream signaling molecules TBK1 and IRF3. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human cervical cancer cells HeLa were treated with CCCP (20 μM) for 30 min, and the effect on the mitochondria-labeled fluorescent dye DiOC6 was observed using live cell fluorescence microscopy. RESULTS: CCCP-induced loss of mitochondrial membrane potential resulted in efflux of DiOC6 from mitochondria into the cytoplasm and subsequent localization to punctate structures. [1] METHODS: Mouse alveolar epithelial cells, MLE-12, were treated with CCCP (10-50 μM) for 2-18 h. The expression levels of the target proteins were examined by Western Blot. RESULTS: CCCP caused a dose- and time-dependent conversion of LC3-I to LC3-II. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To assay in vivo activity, CCCP (5 mg/kg) was administered as a single intraperitoneal injection to adult and aged C57BL/6J mice, and hearts were collected 12 h later. RESULTS: Under CCCP-treated conditions, more mitochondria bound to autophagic vesicles were found in the hearts of adult but not aged mice. [3] METHODS: To assay in vivo activity, CCCP (1 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to mt-Rosella mice once a day for three days. RESULTS: Mitochondrial fragments were readily visible on the hearts of CCCP-treated mice, and these fragments were trapped in lysosomes for degradation.CCCP induced mitochondrial autophagy. [4] |
| Alias | Carbonyl Cyanide m-Chlorophenylhydrazone, Carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone |
| Molecular Weight | 204.62 |
| Formula | C9H5ClN4 |
| Cas No. | 555-60-2 |
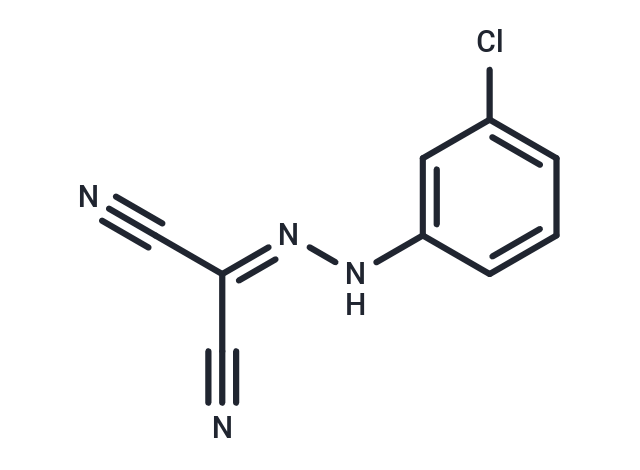
| Smiles | ClC1=CC=CC(N\N=C(/C#N)C#N)=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.3807 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 60 mg/mL (293.23 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 5 mg/mL (24.44 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 6 mg/mL (29.32 mM), Suspension. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.