- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
DL-Penicillamine
DL-Penicillamine (3-Sulfanylvaline) is a chelating agent recommended for the removal of excess copper in patients with Wilson's disease. DL-Penicillamine is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is the most characteristic degradation product of the penicillin antibiotics. It is used as an antirheumatic and as a chelating agent in Wilson's disease. From in vitro studies which indicate that one atom of copper combines with two molecules of DL-penicillamine. DL-Penicillamine also reduces excess cystine excretion in cystinuria. This is done, at least in part, by disulfide interchange between DL-penicillamine and cystine, resulting in the formation of penicillamine-cysteine disulfide, a substance that is much more soluble than cysteine and is excreted readily. DL-Penicillamine interferes with the formation of cross-links between tropocollagen molecules and cleaves them when newly formed. The mechanism of action of DL-penicillamine in rheumatoid arthritis is unknown although it appears to suppress disease activity. Unlike cytotoxic immunosuppressants, DL-penicillamine markedly lowers IgM rheumatoid factor but produces no significant depression in absolute levels of serum immunoglobulins. Also unlike cytotoxic immunosuppressants which act on both, DL-penicillamine in vitro depresses T-cell activity but not B-cell activity.
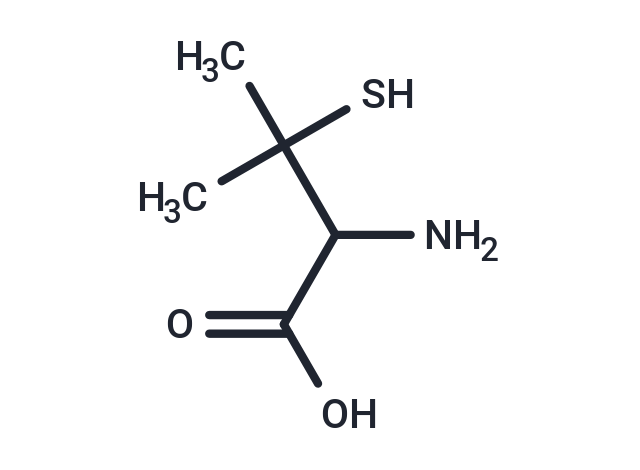
DL-Penicillamine
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $32 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $68 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $109 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $143 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $201 | In Stock |
Product Introduction
| Description | DL-Penicillamine (3-Sulfanylvaline) is a chelating agent recommended for the removal of excess copper in patients with Wilson's disease. DL-Penicillamine is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is the most characteristic degradation product of the penicillin antibiotics. It is used as an antirheumatic and as a chelating agent in Wilson's disease. From in vitro studies which indicate that one atom of copper combines with two molecules of DL-penicillamine. DL-Penicillamine also reduces excess cystine excretion in cystinuria. This is done, at least in part, by disulfide interchange between DL-penicillamine and cystine, resulting in the formation of penicillamine-cysteine disulfide, a substance that is much more soluble than cysteine and is excreted readily. DL-Penicillamine interferes with the formation of cross-links between tropocollagen molecules and cleaves them when newly formed. The mechanism of action of DL-penicillamine in rheumatoid arthritis is unknown although it appears to suppress disease activity. Unlike cytotoxic immunosuppressants, DL-penicillamine markedly lowers IgM rheumatoid factor but produces no significant depression in absolute levels of serum immunoglobulins. Also unlike cytotoxic immunosuppressants which act on both, DL-penicillamine in vitro depresses T-cell activity but not B-cell activity. |
| Alias | 3-Sulfanylvaline |
| Molecular Weight | 149.21 |
| Formula | C5H11NO2S |
| Cas No. | 52-66-4 |
| Smiles | CC(C)(S)C(N)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.204g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 5 mM DMSO: Insoluble | |||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||
H2O
| ||||||||||||||||
Calculator
In Vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Dose Conversion
Tech Support

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.



