Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Deferoxamine Mesylate (DFOM) is an iron chelator and ferroptosis inhibitor. Deferoxamine Mesylate binds free iron into a stable complex and reduces iron accumulation. Deferoxamine Mesylate up-regulates HIF-1α levels and induces apoptosis.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $31 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $48 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $78 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $145 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock |
| Description | Deferoxamine Mesylate (DFOM) is an iron chelator and ferroptosis inhibitor. Deferoxamine Mesylate binds free iron into a stable complex and reduces iron accumulation. Deferoxamine Mesylate up-regulates HIF-1α levels and induces apoptosis. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human cervical cancer cells HeLa were treated with Deferoxamine Mesylate (3-100 μM) for 72 h, and cell numbers were detected using the Incucyte HD imaging system.
RESULTS: Deferoxamine Mesylate inhibited cell growth in a concentration-dependent manner, and significant growth inhibition was observed at 100 μM. [1] METHODS: Human colorectal cancer cells HT29 and HCT116 were treated with Deferoxamine Mesylate (50-200 μM) for 48 h, and the expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Deferoxamine Mesylate induced significant expression of HIF-1α in a dose-dependent manner. [2] METHODS: Human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 were treated with Deferoxamine Mesylate (200 μM) for 24 h. Apoptosis was detected by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: After Deferoxamine Mesylate treatment, the apoptosis rate of MDA-MB-231 cells was unchanged compared with untreated cells, while apoptosis of MCF-7 cells was significantly increased. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To investigate whether Deferoxamine Mesylate reduces inflammation and atherosclerosis in experimental mice, Deferoxamine Mesylate (100 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to apolipoprotein E-deficient (apoE-/-) mice once a day for 10 weeks.
RESULTS: Deferoxamine Mesylate reduced the development of aortic atherosclerotic lesions by 26% Deferoxamine Mesylate also reduced serum MCP-1 levels and gene expression of proinflammatory and macrophage markers in the aorta and heart, and increased protein expression of transferrin receptors in the heart and liver. In contrast, Deferoxamine Mesylate treatment had no effect on serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels. [4] METHODS: To study the effect of Deferoxamine Mesylate on adipocyte dysfunction in adipose tissue of ob/ob mice epididymis, Deferoxamine Mesylate (100 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally into ob/ob mice once daily for fifteen days. RESULTS: Deferoxamine Mesylate significantly improved important parameters of adipose tissue biology by decreasing the secretion of reactive oxygen species and inflammatory markers, by increasing the levels of antioxidant enzymes, HIF-1α, and HIF-1α-targeted proteins, and by altering adipocyte iron-, glucose-, and lipid-related metabolic proteins. Meanwhile, hypertrophic adipocytes were reduced in size and insulin signaling pathway-related proteins were activated after Deferoxamine Mesylate treatment. [5] |
| Cell Research | After cells were seeded onto the collagen-GAG discs and allowed to adhere for 3?hours, they were placed into a hypoxic incubator with 1% O2 or incubated under standard cell culture conditions with deferoxamine mesylate (DFO) added to final concentrations of 30, 60, or 120?μM. Scaffolds seeded with AdMSCs cultured under standard conditions were used as a control [3]. |
| Animal Research | The animals were divided into 4 groups: sham, SAH, SAH+vehicle and SAH+DFX (100mg/kg) group. DFX was administered intraperitoneally 2 and 6 hours after hemorrhage followed by every 12 hours for a maximum of 7 days. The same time course and dosage of saline were administered in the SAH+vehicle group. Afterward, rats underwent behavioral testing and were euthanized at day 1, 3, 7 and 28 for brain water content calculation, immunohistochemistry or western blot assays. The study was performed in three parts. Part 1 measured the brain water content, Evan's blue extravasation, and ultrastructural abnormalities at day 1, 3 and 7 after SAH to evaluate the time-dependent changes in brain edema and BBB disruption (n = 4 per time point and group). Part 2 investigated the role of iron in SAH-induced BBB disruption at day 1, 3 and 7 by brain water content (n = 4, per time point and group), Evan's blue extravasation (n = 4, per time point and group), transmission electron microscopy (n = 4, per time point and group), immunohistochemistry (n = 4, per time point and group) and western blot analysis (n = 3, per time point and group). Part 3 compared the acute (n = 61, per group at day 1; n = 42, per group at day 3; n = 23, per group at day 7) and long term (n = 4, per group at day 28) neurological function after SAH in each group to determine the effect of iron chelation on SAH-induced neurologic impairment [4]. |
| Alias | DFOM, Desferrioxamine B mesylate |
| Molecular Weight | 656.79 |
| Formula | C26H52N6O11S |
| Cas No. | 138-14-7 |
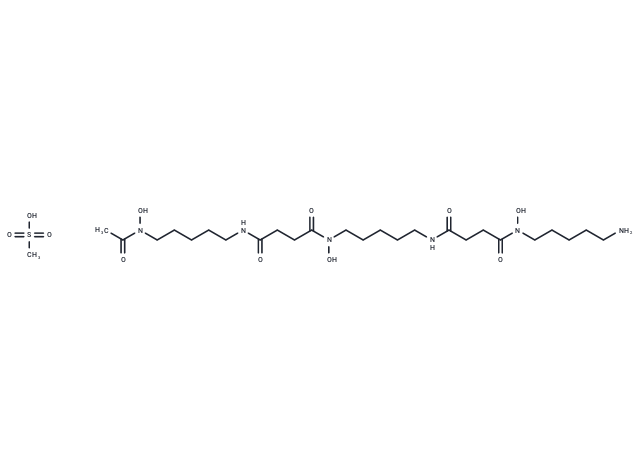
| Smiles | CS(O)(=O)=O.CC(=O)N(O)CCCCCNC(=O)CCC(=O)N(O)CCCCCNC(=O)CCC(=O)N(O)CCCCCN |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | store at low temperature,keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 152.3 mM H2O: 20.83 mg/mL (31.72 mM) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.