Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Desloratadine (Sch34117) is a long-acting piperidine derivate with selective H1 antihistaminergic and non-sedating properties. Desloratadine diminishes the typical histaminergic effects on H1-receptors in bronchial smooth muscle, capillaries and gastrointestinal smooth muscle, including vasodilation, bronchoconstriction, increased vascular permeability, pain, itching and spasmodic contractions of gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Desloratadine is used to provide symptomatic relieve of allergic symptoms.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $35 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $46 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $63 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $101 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $241 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $383 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $52 | In Stock |
| Description | Desloratadine (Sch34117) is a long-acting piperidine derivate with selective H1 antihistaminergic and non-sedating properties. Desloratadine diminishes the typical histaminergic effects on H1-receptors in bronchial smooth muscle, capillaries and gastrointestinal smooth muscle, including vasodilation, bronchoconstriction, increased vascular permeability, pain, itching and spasmodic contractions of gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Desloratadine is used to provide symptomatic relieve of allergic symptoms. |
| Targets&IC50 | H1 receptor:51 nM |
| In vitro | Desloratadine inhibits histamine-induced paw edema in mice, with an ED50 of 0.15 mg/kg, and exhibits dose-dependent and sustained mydriasis in guinea pigs in vivo at concentrations of 1 mg/mL, 3 mg/mL, and 10 mg/mL. It also suppresses the increase in vascular permeability in guinea pigs caused by histamine assault on the upper respiratory tract, with an ED50 of 0.9 μg. Furthermore, 5 mg/kg desloratadine counteracts the disruption of the blood-brain barrier in awake mice, thereby inhibiting tremors induced by the tremogenic agent oxotremorine. |
| In vivo | Desloratadine acts as a competitive antagonist to carbachol-induced contractions in isolated rabbit iris sphincter muscles, with a pA2 of 6.67. It binds to the human H1 receptor with a Ki value of 0.87 nM, displacing tritiated mepyramine. In competitive binding studies, Desloratadine was found to be more effective than cetirizine, ebastine, fexofenadine, and loratadine by factors of 52, 57, 194, and 153, respectively. Desloratadine (0.1 μM to 10 μM) also inhibits platelet-activating factor-induced chemotaxis and TNF-α-induced adhesion of eosinophils in patients with allergic rhinitis or asthma. Furthermore, it dose-dependently reduces IL-13 secretion from human basophils activated by IL-3 and PMA across the same concentration range. Pre-treatment with Desloratadine at 10 μM results in an approximately 80% reduction in anti-IgE-induced accumulation of IL-4 messages in cultured basophils. [3H]Desloratadine binds to human histamine H1 receptors expressed in CHO cells with a Kd of 1.1 nM. Concentrations of Desloratadine ranging from 100 nM to 10 μM were found to inhibit both IgE-mediated and non-IgE-mediated production of cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 in human basophils. Additionally, Desloratadine at 300 nM to 100 μM inhibits the release of histamine from human peripheral blood basophils stimulated by both IgE-mediated and non-IgE-mediated pathways. |
| Alias | Sch34117, NSC 675447 |
| Molecular Weight | 310.82 |
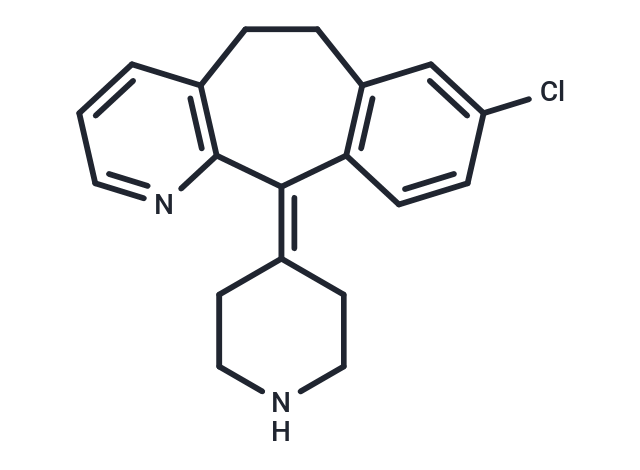
| Formula | C19H19ClN2 |
| Cas No. | 100643-71-8 |
| Smiles | ClC1=CC2=C(C=C1)\C(=C1\CCNCC1)C1=C(CC2)C=CC=N1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.221 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 31.1 mg/mL (100 mM) DMSO: 40 mg/mL (128.69 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.