Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate ammonium (1-Pyrrolidinedithiocarboxylic acid ammonium salt), a selective NF-κB inhibitor, inhibits translation of nitric oxide synthase mRNA to prevent induction.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $58 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $96 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock |
| Description | Pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate ammonium (1-Pyrrolidinedithiocarboxylic acid ammonium salt), a selective NF-κB inhibitor, inhibits translation of nitric oxide synthase mRNA to prevent induction. |
| In vitro | Pretreatment of cells with PDTC (3-1000 mM) dose-dependently attenuate IL-8 production. Furthermore, PDTC (100 mM) suppresses the accumulation of IL-8 mRNA. PDTC inhibites the activation of NF-kB, because PDTC suppresses both NF-kB DNA binding and NF-kB-dependent transcriptional activity. Taken together, our data demonstrate that NF-kB inhibition with PDTC decrease IL-8 production by intestinal epithelial cells[1]. |
| In vivo | The DSS+PDTC-treated groupⅡ exhibited suppression of shortening of intestinal length and reduction of DAI score. Activated NF-κB level and IL-1β and TNF-α levels are significantly lower in DSS+PDTC-treated groupⅡ. These findings suggest that suppression of NF-κB activity by PDTC can delay the healing of mucosal tissue defects (erosions or ulcers) arising from inflammation, but that it can strongly suppress the expression of inf-lammatory cytokines (IL-1β and TNF-α), resulting in significant alleviation of colitis. PDTC is useful for the treatment of ulcerative colitis[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | All binding studies are performed in an HTRF assay buffer consisting of dPBS supplemented with 0.1% (with v) bovine serum albumin and 0.05% (v/v) Tween-20. For the PD-l-Ig/PD-Ll-His binding assay, inhibitors are pre-incubated with PD-Ll-His (10 nM final) for 15 m in 4 μL of assay buffer, followed by addition of PD-l-Ig (20 nM final) in 1 μL of assay buffer and further incubation for 15 m. PD-L1 from either human, cyno, or mouse are used. HTRF detection is achieved using europium crypate-labeled anti- Ig (1 nM final) and allophycocyanin (APC) labeled anti-His (20 nM final). Antibodies are diluted in HTRF detection buffer and 5 μL is dispensed on top of binding reaction. The reaction mixture is allowed to equilibrate for 30 minutes and signal (665 nm/620 nm ratio) is obtained using an En Vision fluorometer. Additional binding assays are established between PD-1-Ig/PD-L2-His (20, 5 nM, respectively), CD80-His/PD-Ll-Ig (100, 10 nM, respectively) and CD80-His/CTLA4-Ig (10, 5 nM, respectively). |
| Cell Research | The human colon cancer cell line HT-29 is obtained and cells are grown in modified McCoy's 5A medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. To study the effect of PDTC on IL-8 production, HT-29 cells in 96-well plates are induced with 20 ng/mL of IL-1b for 18 h. Various concentrations (3-1000 mM) of PDTC or its vehicle (culture medium) are added to the cells 30 min prior to IL-1b stimulation. The concentration of IL-8 in the supernatant is determined using solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, as described previously employing the multiple antibody sandwich principle that specifically detects human IL-8[1]. |
| Alias | PDTC ammonium, APDC, Ammonium pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate, 1-Pyrrolidinedithiocarboxylic acid ammonium salt |
| Molecular Weight | 164.29 |
| Formula | C5H12N2S2 |
| Cas No. | 5108-96-3 |
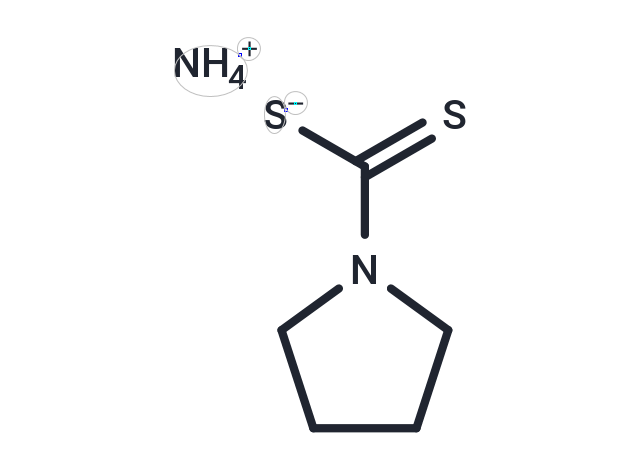
| Smiles | [NH4+].[S-]C(=S)N1CCCC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.117 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 75 mg/mL (456.51 mM), Sonication is recommended. 5% DMSO+95% Saline: 0.6 mg/mL (3.65 mM), In vivo: Please add co-solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5% DMSO+95% Saline/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.