Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Benzocaine is a surface anesthetic that acts by preventing transmission of impulses along nerve fibers and at nerve endings.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $35 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock |
| Description | Benzocaine is a surface anesthetic that acts by preventing transmission of impulses along nerve fibers and at nerve endings. |
| Targets&IC50 | Na+ channel:0.8 mM (IC50) |
| In vitro | Benzocaine blocks μ1 wild-type Na+ currents in a dose-dependent manner, with an IC50 of 0.8 mM in HEK293T cells. At 1 mM, Benzocaine inhibits approximately 55% of wild-type Na+ current, about 95% of μ1-N1584A mutant current, and about 80% of μ1-I1575A mutant current. [1] Benzocaine produces a biphasic (protective/inductive) concentration-dependent hemolytic effect on rat erythrocytes, with effective Benzocaine:lipid molar ratios in the membrane for protection (RePROT), onset of hemolysis (ReSAT), and 100% membrane solubilization (ReSOL) at 1.0:1, 1.1:1, and 1.3:1, respectively. [2] During repetitive pulses, Benzocaine and 4-hydroxybenzoate interact with the open and inactivated channels, but the complex dissociates too rapidly during interpulse to achieve a significant use-dependent Na+ current block. [3] Benzocaine (500 μM) reduces peak and steady-state currents and increases the amplitude of the inactivating component from 21.7% to 30.2% (n=7, P<0.05), resulting in an average block of 30.9% at the end of pulses to +60 mV (n=7). It also significantly accelerates the initial phase of deactivation (τf=27.2±2.6 ms, n=7, P<0.01) without affecting the slow phase of tail current decline. Benzocaine binds with high affinity to an intracellular site producing 'agonist' effects and a low-affinity subsite in the inner mouth producing blocking effects. Benzocaine and extracellular K(+) interact to alter the voltage-dependence of channel opening. [4] |
| In vivo | Benzocaine is absorbed rapidly and similarly through both viable and nonviable skin of the hairless guinea pig, the absorption of the two acidic compounds, benzoic acid and PABA, is greater through nonviable skin. [5] |
| Molecular Weight | 165.19 |
| Formula | C9H11NO2 |
| Cas No. | 94-09-7 |
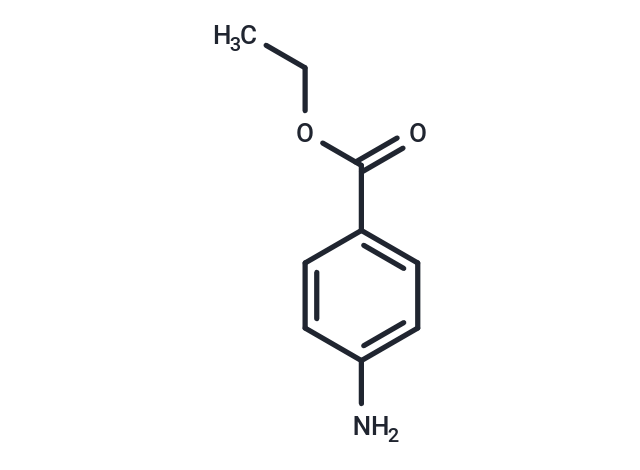
| Smiles | CCOC(=O)C1=CC=C(N)C=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.17 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (302.68 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 31 mg/mL (187.66 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.