- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty
Shopping Cart
Bifonazole
Catalog No. T1187Cas No. 60628-96-8
Alias Bay H-4502
Bifonazole (Bay H-4502) acts to destabilize the fungal cytochrome p450 51 enzyme (also known as Lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase). It works by inhibiting the production of a substance called ergosterol, which is an essential component of fungal cell membranes. This is vital in the cell membrane structure of the fungus. Its inhibition leads to cell lysis. The disruption in production of ergosterol disrupts the cell membrane and causes holes to appear. The cell membranes of fungi are vital for their survival. They keep unwanted substances from entering the cells and stop the contents of the cells from leaking out.
Bifonazole
Catalog No. T1187Alias Bay H-4502Cas No. 60628-96-8
Bifonazole (Bay H-4502) acts to destabilize the fungal cytochrome p450 51 enzyme (also known as Lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase). It works by inhibiting the production of a substance called ergosterol, which is an essential component of fungal cell membranes. This is vital in the cell membrane structure of the fungus. Its inhibition leads to cell lysis. The disruption in production of ergosterol disrupts the cell membrane and causes holes to appear. The cell membranes of fungi are vital for their survival. They keep unwanted substances from entering the cells and stop the contents of the cells from leaking out.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $31 | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $70 | In Stock | |
| 10 g | $98 | Backorder |
Bulk & Custom
Add to Cart
Questions
View MoreSelect Batch
Purity:99.87%
Contact us for more batch information
All TargetMol products are for research purposes only and cannot be used for human consumption. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use TargetMol products for any other purpose.Product Introduction
Bioactivity
Chemical Properties
| Description | Bifonazole (Bay H-4502) acts to destabilize the fungal cytochrome p450 51 enzyme (also known as Lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase). It works by inhibiting the production of a substance called ergosterol, which is an essential component of fungal cell membranes. This is vital in the cell membrane structure of the fungus. Its inhibition leads to cell lysis. The disruption in production of ergosterol disrupts the cell membrane and causes holes to appear. The cell membranes of fungi are vital for their survival. They keep unwanted substances from entering the cells and stop the contents of the cells from leaking out. |
| In vitro | Bifonazole, a broad spectrum antifungal agent, inhibits monooxygenase activity and induces a type II binding spectrum in 2B4dH(H226Y), a modified enzyme previously crystallized in the presence of 4-(4-chlorophenyl)imidazole (CPI). [1] Bifonazole (40 mM) releases Ca2+ from the store sensitive to 1 mM thapsigargin, an endopolasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump inhibitor. Bifonazole (40 mM) per se induces capacitative Ca2+ entry while reduces 1 mM thapsigargin-induced capacitative Ca2+ entry. [2] Bifonazole is calmodulin antagonists which most effectively reduce glycolysis and ATP level in B16 melanoma cells. Bifonazole acts through allosteric regulation and detachment of glycolytic enzymes from cytoskeleton. [3] Bifonazole blocks PGE2 formation induced by 2 μm and 4 μm arachidonic acid clearly better than at 6 or 10 μm of the agonist. Bifonazole shows the same characteristics in MC3T3-E1 and UMR-106 cells stimulated by ionomycin or various concentrations of arachidonic acid. [4] |
| In vivo | Bifonazole, but not clotrimazole, exhibits the characteristics of a peroxisome proliferator including hepatomegaly (increase in liver:body weight ratio), up to a 4-fold induction of lauric acid omega-hydroxylase activity and an 8-fold induction of palmitoyl-CoA oxidation by rat liver peroxisomes. Bifonazole also induces P402B1/2B2, P4503A and P4501A1, but not P4502E1. [5] |
| Alias | Bay H-4502 |
| Molecular Weight | 310.39 |
| Formula | C22H18N2 |
| Cas No. | 60628-96-8 |
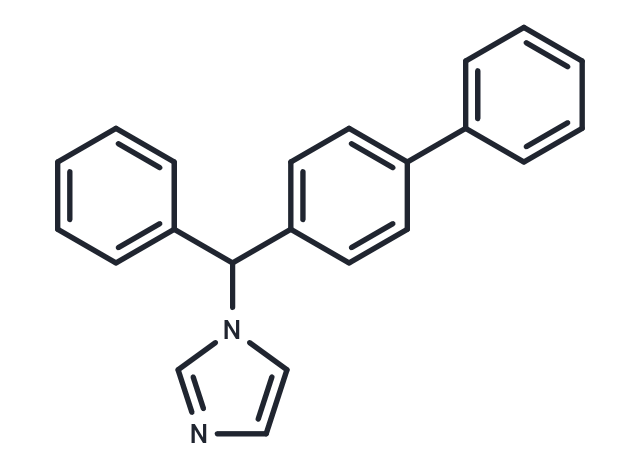
| Smiles | C(C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC=CC=C2)(N3C=CN=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4 |
| Relative Density. | 1.1150 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
Storage & Solubility Information
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 1.55 mg/mL (4.99 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: 16 mg/mL (51.55 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/Ethanol
Ethanol
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Calculator
In Vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Please enter your animal experiment information in the following box and click Calculate to obtain the mother liquor preparation method and in vivo formula preparation method:
Mother liquor preparation method: 2 mg of drug dissolved in 50 μL DMSO (mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
(mother liquor concentration of 40 mg/mL), if you need to configure a concentration that exceeds the solubility of the product, please contact us first.
Preparation method for in vivo formula: Take 50 μL DMSO main solution, add 300 μLPEG300
main solution, add 300 μLPEG300 mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O
mix well and clarify, then add 50 more μL Tween 80, mix well and clarify, then add 600 more μLddH2O mix well and clarify
mix well and clarify
For Reference Only. Please develop an appropriate dissolution method based on your laboratory animals and route of administration.
Dose Conversion
You can also refer to dose conversion for different animals. More Dose Conversion
Tech Support
Please see Inhibitor Handling Instructions for more frequently ask questions. Topics include: how to prepare stock solutions, how to store products, and cautions on cell-based assays & animal experiments, etc
Related Tags: buy Bifonazole | purchase Bifonazole | Bifonazole cost | order Bifonazole | Bifonazole chemical structure | Bifonazole in vivo | Bifonazole in vitro | Bifonazole formula | Bifonazole molecular weight

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.




