Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

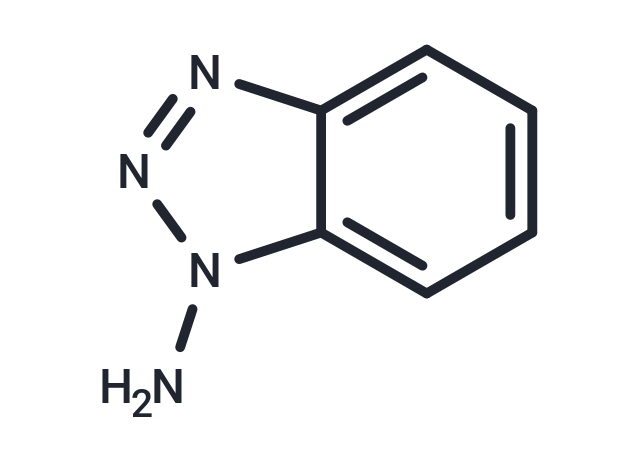
1-Aminobenzotriazole (ABT) (ABT) is a non-specific cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibitor.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $48 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $57 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $101 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $45 | In Stock |
| Description | 1-Aminobenzotriazole (ABT) (ABT) is a non-specific cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibitor. |
| In vitro | In vitro, 1-Aminobenzotriazole rapidly and efficiently destroyed P450 in both hepatic and renal microsomes prepared from naive male Sprague-Dawley rats.Incubation of hepatic or renal microsomes in vitro with 1-Aminobenzotriazole produced detectable destruction of P450 within 5 min. Maximal destruction of P450 occurred within 10 min in both hepatic and renal microsomes during in vitro incubation with 1-Aminobenzotriazole. 1-Aminobenzotriazole-induced destruction of P450 in vitro was concentration-dependent.For hepatic microsomes, maximal destruction of about 70% of P450 required concentrations of 1-Aminobenzotriazole equal to or greater than 10 mM. For renal microsomes, maximal destruction of about 80% of P450 required concentrations of 1-Aminobenzotriazole equal to or greater than 10 mM. In both liver and kidney, only P450 content and P450-dependent activities were significantly decreased[1]. |
| In vivo | Hepatic and renal microsomes and cytosol were prepared from male Sprague-Dawley rats following 1-Aminobenzotriazole pretreatment (0-100 mg/kg ip) for various times.Administration of 100 mg 1-Aminobenzotriazole/kg produced profound reductions in P450 content in both liver and kidney within 2 hr;loss of P450 in both tissues persisted for at least 48 hours.1-Aminobenzotriazole-induced destruction of P450 was dose-dependent.Maximal destruction of about 80% of total hepatic P450 occurred at dosages of 1-Aminobenzotriazole equal to or greater than 10 mg/kg.Maximal destruction of about 80% of total renal P450 occurred at dosages of 1-Aminobenzotriazole equal to or greater than 50 mg/kg[1]. |
| Cell Research | Animals were killed by cervical dislocation and decapitation.?Kidneys and livers were excised quickly and placed in ice cold 1.15% KC].?Renal inner medulla and papilla were discarded.?Renal cortex and liver were minced and homogenized in 3 vol of 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) containing 250 mM sucrose and 1.5 mM EDTA.?Kidney and liver homogenates were centrifuged at 10000g for 20 min. The resulting supematant was centrifuged at 105000g for 60 min. The 105000g supematant (cytosol) was used for the determination of glutathione S-transferase activity .?The microsomal fraction (pellet) was resuspended in phosphate buffered sucrose (pH 7.4) and centrifuged at 105000g for 60 min. The resulting microsomal fraction was resuspended in phosphate-buffered sucrose (pH 7.4) containing 20% glycerol to a final concentration of l0-20 mg protein per milliliter.?The microsomal fraction was used for the determination of P450, cytochrome b5, and NADPH-cytochrome-c reductase activities.?Microsomes from control or ABT-treated rats were either analyzed on the day of preparation or stored overnight at -80 C. In all cases, control microsomes were handled identically with ABT-treated microsomes.?P450 content in control and ABT-treated microsomes was not affected by overnight storage[1]. |
| Animal Research | For in vivo experiments, rats received ABT (O-100 mg/kg) dissolved in normal saline at a concentration of I-50 mg/ml.?ABT was administered ip and rats were killed at various times thereafter.?Total injection volume was either 1 or 2 ml/kg and control rats received 2 ml saline/kg[1]. |
| Alias | ABT, 3-Aminobenzotriazole |
| Molecular Weight | 134.14 |
| Formula | C6H6N4 |
| Cas No. | 1614-12-6 |
| Smiles | NN1C=2C(=CC=CC2)N=N1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.2769 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 125 mg/mL (931.86 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.