Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Betaxolol hydrochloride (SL 75212 HCl) is a cardioselective beta-blocker used in the treatment of hypertension.Betaxolol hydrochloride has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent drug induced liver injury.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $32 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $46 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $77 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $162 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $29 | In Stock |
| Description | Betaxolol hydrochloride (SL 75212 HCl) is a cardioselective beta-blocker used in the treatment of hypertension.Betaxolol hydrochloride has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent drug induced liver injury. |
| Targets&IC50 | β1-adrenoceptor:6 μM |
| In vitro | Betaxolol's constituents are capable of partially inhibiting changes induced by NMDA and hypoxia/glucose deficiency. Intraperitoneal injection of Betaxolol in rats during focal ischemia and before reperfusion injury effectively mitigates alterations in calretinin and ChAT immunoreactivity, and also prevents the decline of b-wave amplitude. |
| In vivo | At a concentration of 10 µM, Betaxolol significantly inhibits the release of LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) induced by glutamate esters. Additionally, 100 µM Betaxolol effectively prevents the release of LDH in cortical tissue caused by hypoxia. Betaxolol offers protective effects on retinal neurons and attenuates the influx of ^(45)Ca2+ induced by NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) when β-adrenergic receptor agonists are ineffective. |
| Cell Research | Dissociated cortical cells from 16–18-day-old fetal rats are grown, in 35 mm dishes, in DMEM supplemented with L-glutamine (4 mM), glucose (6 g/L), penicillin (100 U/mL), streptomycin (100 μg/mL) and 10% hormonal supplemented medium consisting of transferrin (1 mg/mL), insulin (250 μg/mL) putrescine (600 μM), sodium selenite (0.3 μM), progesterone (0.2 μM) and estradiol (0.1 pM) for 7 days in an atmosphere of 5% CO2/95% O2 at 37 °C. The cultures are then transferred to a culture medium which lacks the hormonal supplemented medium. L-glutamate is added to the medium and incubated for a further 4 hours under normoxic conditions. Betaxolol are added to the cultures at the same time as L-glutamate. In other experiments the cultures are subjected to anoxic conditions, 95% N2/5% CO2, for 5 hours at 37 °C. Betaxolol is added prior to anoxia. Reoxygenation is then achieved by replacing the cells in normoxic conditions (95% O2/5% CO2) for 3 hours. Cellular injury is assessed by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release into the cell culture supernatant after hypoxia/reoxygenation or glutamate exposure. LDH activity is assayed spectrophotometrically by following NADH metabolism for 2 minutes at 340 nm.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | SL 75212 HCl, Betaxolol HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 343.89 |
| Formula | C18H30ClNO3 |
| Cas No. | 63659-19-8 |
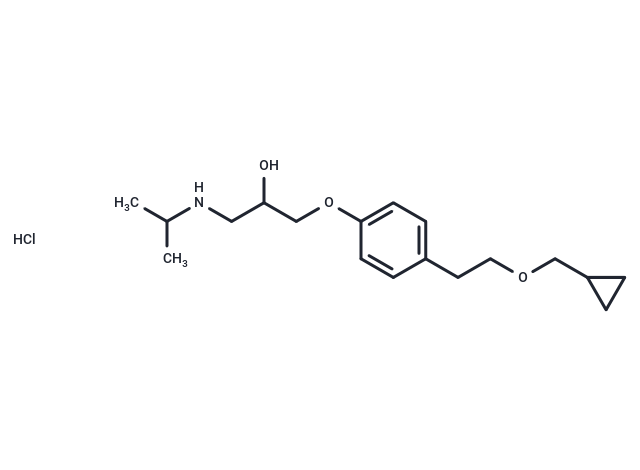
| Smiles | Cl.CC(C)NCC(O)COc1ccc(CCOCC2CC2)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (145.4 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 29.08 mM, Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.