Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

DMOG (Dimethyloxalylglycine), an antagonist of the α-ketoglutarate cofactor, is an inhibitor for HIF prolyl hydroxylase.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $58 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $90 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $162 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | DMOG (Dimethyloxalylglycine), an antagonist of the α-ketoglutarate cofactor, is an inhibitor for HIF prolyl hydroxylase. |
| In vitro | DMOG shows only weakly active in the microsomal system, but efficiently suppresses hydroxyproline synthesis in intact cells. [1] DMOG reduces FGF-2-induced proliferation and cyclin A expression by inhibiting prolyl hydroxylase activity in HPASMC. [3] |
| In vivo | DMOG inhibits endogenous HIF inactivation and induces angiogenesis in the ischaemic skeletal muscles of mice. [2] Up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α by DMOG may be the cardioprotective mechanism of ischemic postconditioning in hyperlipidemic rats[4]. |
| Cell Research | To analyze DNA synthesis as an index of cellular proliferation, VSMC are plated in 48-well plates (5,000 per square centimeter) in growth medium, incubated overnight, and serum-deprived (1% FCS) for 24 h. Replicate wells are then stored at −70°C for baseline (day 0) cell counts, and fresh medium with or without growth factors is added to the remaining wells, which are incubated 72-96 h in 20 or 5% O2. Days 0 and 3 or 4 cell counts are determined by lysing cells in a buffer containing a fluorescent dye, which has minimal fluorescence by itself but fluoresces when bound to DNA or RNA. Absolute cell numbers are calculated by comparing the fluorescence of specimens with that of a standard curve similarly prepared using a known number of cells. (Only for Reference) |
| Alias | Dimethyloxalylglycine, Dimethyloxaloylglycine, Dimethyloxallyl Glycine |
| Molecular Weight | 175.14 |
| Formula | C6H9NO5 |
| Cas No. | 89464-63-1 |
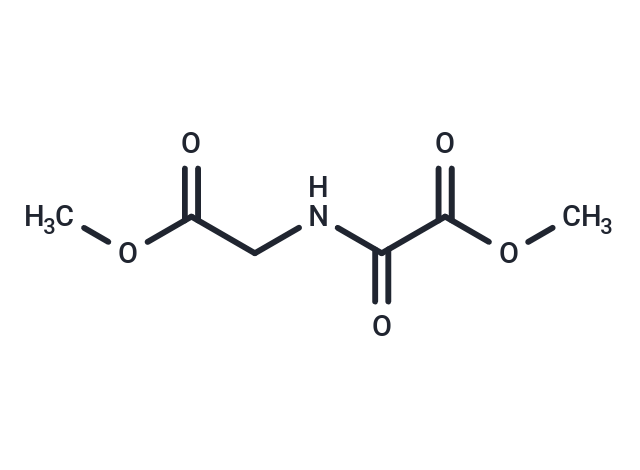
| Smiles | COC(=O)CNC(=O)C(=O)OC |
| Relative Density. | 1.247g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 17.54 mg/mL (100 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 60 mg/mL (342.58 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 35 mg/mL (199.84 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.