Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Docetaxel (RP-56976), a semi-synthetic analog of paclitaxel, is a microtubule depolymerization inhibitor (IC50=0.2 μM) that attenuates the effects of bcl-2 and bcl-xL gene expression and exhibits apoptosis-inducing, anti-tumor activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $57 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $82 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $136 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $197 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $52 | In Stock |
| Description | Docetaxel (RP-56976), a semi-synthetic analog of paclitaxel, is a microtubule depolymerization inhibitor (IC50=0.2 μM) that attenuates the effects of bcl-2 and bcl-xL gene expression and exhibits apoptosis-inducing, anti-tumor activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | Microtubule:0.2 μM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human lung cancer cells NCI-H460 were treated with Docetaxel (0.2-200 nmol/L) for 24-72 h, and cell viability was measured by MTS. RESULTS: The IC50 of NCI-H460 to Docetaxel was 0.030 μmol/L at 72 h and 0.116 μmol/L at 24 h. [1] METHODS: Human prostate cancer cells PC-3, DU-145 and LNCaP were treated with Docetaxel (0.5-4 nM) for 48 h. Apoptosis was detected by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: High-dose Docetaxel treatment significantly increased the proportion of Annexin V+ apoptotic cells. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To detect anti-tumor activity in vivo, Docetaxel (5-10 mg/kg) and PD-1 inhibitor (200 μg/only) were intraperitoneally injected into CB17 SCID mice carrying mouse prostate cancer tumor RM-1 five times a week for ten days. RESULTS: PD-1 inhibitor combined with Docetaxel had a synergistic effect on prostate cancer in mice, inhibiting the growth of prostate tumors, increasing the survival rate and reducing adverse effects. [3] METHODS: To assay antitumor activity in vivo, Docetaxel (7.5-15 mg/kg, intratumorally injected IT twice weekly for six weeks; or 20-40 mg/kg weekly intravenously injected IV) was administered to C57BL/6 mice harboring HNSCC tumors HN30 or HN12. RESULTS: IT Docetaxel improved overall survival and disease-free survival and reversed tumor growth. At equivalent dose levels, IT Docetaxel resulted in 26-fold higher peak tumor concentrations and 24-fold longer tumor exposure than IV treatment. [4] |
| Cell Research | NCI-H460 cells (4 × 10^3) were grown in 100 μl of DMEM medium containing serum per well in a 96-well plate. After 24 h, the cells were treated with docetaxel (0, 0.2, 0.63, 2, 6.3, 20, 63 and 200 nmol/L, respectively) for 72 h. Every treatment was triplicate in the same experiment. Then 20 μl of MTS was added to each well for 1 to 4 h at 37°C. After incubation, the absorbance was read at a wavelength of 490 nm according to the manufacturer's protocol. The IC50 calculation was performed with GraphPad Prism 5.0 software [2]. |
| Animal Research | Docetaxel (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 60, and 80 mg/kg per week) was given once a week for 3 weeks for mice. Because more than 30 mg/kg per week of the drug caused body weight loss in mice, 20 mg/kg per week of docetaxel was judged to be the maximum nontoxic dose. Docetaxel (20 mg/kg per week) was given to mice once a week for 3 weeks at one of the following different points (2, 10, 14, or 22 HALO). Seventy-two hours after the final dosing of the agent, the intestinal mucosa of the small intestine (proximal 8 cm) was removed, fixed in 20 N Mildform solution (containing 8% formaldehyde in a buffered solution), and embedded in paraffin blocks, and sections of 5 mm were put on glass slides. Apoptosis was detected using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) method, using the Apop Tag Peroxidase In Situ Apoptosis Detection Kit. Specimens were dewaxed and immersed in phosphate-buffered saline for 5 minutes at room temperature, incubated with 20 mg/ml proteinase K for 15 minutes at room temperature, and then quenched of endogenous peroxidase in 2% hydrogen peroxide in phosphate-buffered saline. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase enzyme was applied directly onto the specimens, which were then incubated at 37°C for 1 hour. The reaction was terminated by transferring the slides to stop/wash buffer for 10 minutes at room temperature, and then specimens were covered with peroxidase-conjugated anti-digoxigenin antibody and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. Specimens were then soaked in staining buffer containing 0.05% diaminobenzidine to achieve color development. Finally, the specimens were counterstained by immersion in Mayer's hematoxylin solution. Apoptotic cells were counted under a light microscope in a good longitudinal crypt section. Starting at the base of the crypt column, the TUNEL-positive cells were counted up to the 18th cell position in each crypt.One hundred crypt sections were scored in each animal, and a frequency of TUNELpositive cells per crypt was calculated. Dosing time-dependent influence of docetaxel on intestinal apoptosis was also examined in female Balb/c mice [5]. |
| Alias | RP-56976, NSC 628503 |
| Molecular Weight | 807.88 |
| Formula | C43H53NO14 |
| Cas No. | 114977-28-5 |
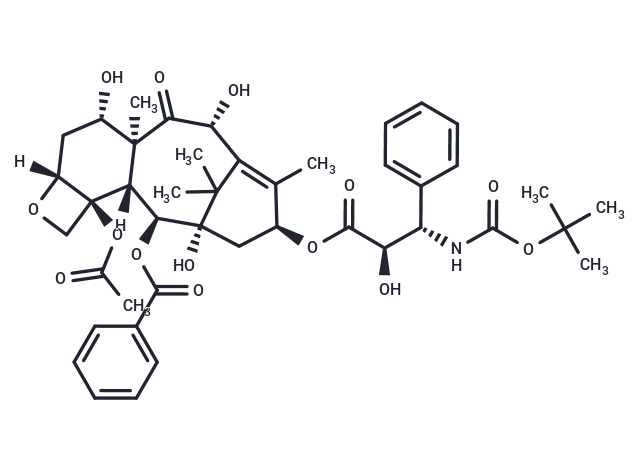
| Smiles | O(C(C)=O)[C@]12[C@]3([C@H](OC(=O)C4=CC=CC=C4)[C@@]5(O)C(C)(C)C([C@@H](O)C(=O)[C@]3(C)[C@@H](O)C[C@]1(OC2)[H])=C(C)[C@@H](OC([C@@H]([C@@H](NC(OC(C)(C)C)=O)C6=CC=CC=C6)O)=O)C5)[H] |
| Relative Density. | 1.38 g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 80.8 mg/mL (100.01 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 60 mg/mL (74.27 mM), Sonication is recommended. 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 8.08 mg/mL (10 mM), suspension.In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/Ethanol
Ethanol
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.