Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

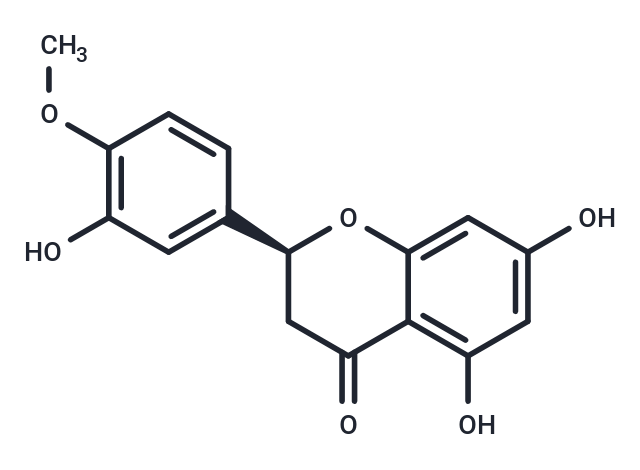
Hesperetin belongs to the flavanone class of flavonoids. Hesperetin, in the form of its glycoside hesperidin, is the predominant flavonoid in lemons and oranges.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $38 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $54 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $80 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Hesperetin belongs to the flavanone class of flavonoids. Hesperetin, in the form of its glycoside hesperidin, is the predominant flavonoid in lemons and oranges. |
| In vitro | Hesperetin has the retention of antioxidant potential in self nano-emulsifying drug delivery system[1]. Hesperetin and NGR display broad-spectrum inhibition against human UGTs. In addition, Hesperetin exhibits strong inhibitory effects on UGT1A1, 1A3 and 1A9 (both IC50 and Ki values lower than 10 μM) and moderately inhibits UGT1A4, UGT1A7, UGT1A8 (IC50 values 29.68-63.87 μM)[2]. Hesperetin interacts with different types of proteins involving hydrogen bonds, pi-pi effects, pi-cation bonding and pi-sigma interactions with varying binding energies. Hesperetin exhibits drug-like properties which indicate its potential as a therapeutic option for CHIKV infection[3]. Hesperetin dose-dependently reduces GCDCA-induced caspase-3 activity in cultured primary rat hepatocytes. Hesperetin also dose-dependently reduces CM-induced Nos2 (iNOS) expression in hepatocytes. Interestingly, hesperetin-induced expression of the antioxidant gene haem oxygenase 1 (HO-1) about fourfold compared with cytokine mixture alone[5]. |
| In vivo | Pre-administration of Hesperetin (40 mg/kg b.w., oral) significantly reduces Cd-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in rats’ brains, while restoring antioxidant activity and membrane-bound enzyme functions, and lessening apoptosis[4]. At a dose of 200 mg/kg, Hesperetin diminishes Con A-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and hepatic Nos2 (iNOS) expression in mice, alongside reducing the presence of apoptotic bodies, hydropic degeneration, nuclear fragments, autolysis, and hemorrhage. Moreover, Hesperetin co-treatment notably lowers the infiltration of leukocytes in the liver tissue of mice suffering from D-GalN/LPS-induced fulminant hepatitis, demonstrating its protective effect in a murine model[5]. |
| Kinase Assay | First, 0.5 mL tissue homogenate is diluted with 1 mL water. Then, to this mixture, 2.5 mL ethanol and 1.5 mL chloroform (all reagents chilled) are added and shaken for 1 min at 4°C, then centrifuged. The enzyme activity in the supernatant is determined. The assay mixture contained 1.2 mL sodium pyrophosphate buffer (0.025 M, pH 8.3), 0.1 mL 186 mM phenazine methosulfate (PMS), 0.3 mL 30 mM Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT), and 0.2 mL of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH), and appropriately diluted enzyme preparation and water in a total volume of 3 mL. Reaction is initiated by the addition of NADH. After incubation at 30°C for 90 min, the reaction is stopped by the addition of 1 mL glacial acetic acid. The reaction mixture is stirred vigorously and shaken with 4 mL n-butanol. The intensity of the chromogen in the butanol layer is measured at 560 nm against a butanol blank. A system without enzyme served as control. One unit of enzyme activity is defined as 50% inhibition of NBT reduction in 1 min under the assay conditions. |
| Molecular Weight | 302.28 |
| Formula | C16H14O6 |
| Cas No. | 520-33-2 |
| Smiles | O=C1C=2C(O[C@@H](C1)C3=CC(O)=C(OC)C=C3)=CC(O)=CC2O |
| Relative Density. | 1.458g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 45 mg/mL (148.87 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.