Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

KN-93 is a selective inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII), competitively blocking CaM binding to the kinase.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $52 | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $72 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $115 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $157 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $322 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $397 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $582 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $129 | In Stock |
| Description | KN-93 is a selective inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII), competitively blocking CaM binding to the kinase. |
| Targets&IC50 | CaMK II:370 nM. (Ki) |
| In vitro | Following 2 days of treatment with KN-93, 95% of cells are halted in the G1 phase, a process which is reversible; one day post KN-93 withdrawal, a notable number of cells transition into the S and G2-M phases. KN-93 effectively inhibits cell growth prompted by various growth factors, including basic fibroblast growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor-BB, epidermal growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor-1, in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts[1]. Moreover, KN-93 disrupts H+, K+-ATPase activity, significantly dissipates the proton gradient across gastric membrane vesicles, and diminishes the luminal space volume[2]. At a concentration of 0.5 μM, KN-93 averts the increase in left ventricular (LV) developed pressure and the occurrence of early afterdepolarizations. It also blocks the rise in Ca2+-independent CaM kinase activity observed during these afterdepolarizations[3]. At a 10 μM concentration, KN-93 significantly suppresses the activation of CaMKII/NF-κB signaling triggered by high glucose levels, leading to a decreased expression of VEGF, iNOS, and ICAM-1 in Müller cells[4]. |
| In vivo | KN-93, administered intraperitoneally at a dosage of 1 mg/kg/day, effectively reduces retinal vascular leakage in diabetes and concurrently inhibits the phosphorylation of CaMKII and NF-κB within the diabetic retina[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | Cells are grown on 12-mm diameter glass coverslips in DMEM 100% serum and various concentrations of KN-93 or KN-92. After 0, 1, 2, and 3 days of culture in the presence of drug, coverslips are removed from culture, rinsed once in PBS, and then submerged in 100% methanol at -20°C for 3 min. Fixed cells are stored in PBS until staining using the TUNEL assay. Cells are overlaid on 20 μL PBS/1 mg/mL BSA for 30 min, rinsed in PBS, and then overlaid on 20 μL containing 100 mM sodium cacodylate (pH 6.8), 1 mM CoCl2, 0.1 mM DTT, 0.1 mg/mL BSA, 20 μM fluorescein-12-dUTP, and 0.1 unit/μL terminal transferase at 37°C for 60 min. Coverslips are rinsed in PBS twice, mounted on slides, and photographed using an OLYMPUS BX5O epifluorescent microscope using a UPLAN APO 40X oil immersion objective. |
| Cell Research | KN-93 is dissolved in DMSO. Cell viability is assessed by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Briefly, Müller cells are seeded at a density of 10×104 cells per well in 96-well plates and cultured until sub-confluence. Next, cells are treated with curcumin for 24 h before incubation with MTT (5 mg/mL) at 37°C in 5% CO2 atmosphere for 4 h. The culture medium is then removed, and the formazan formed in the reaction is dissolved in 150 μL DMSO. The optical density of the solution is measured at 490 nm using a multifunctional microplate reader. Cell viability in each well is presented as a percentage of the control (vehicle-treated group). |
| Molecular Weight | 501.04 |
| Formula | C26H29ClN2O4S |
| Cas No. | 139298-40-1 |
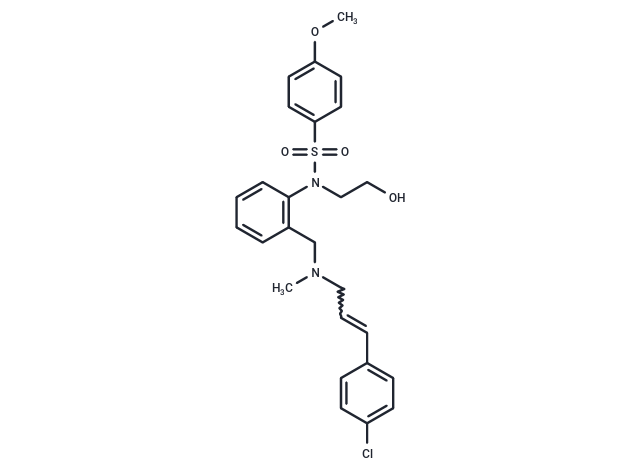
| Smiles | N(S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(OC)C=C1)(CCO)C2=C(CN(CC=CC3=CC=C(Cl)C=C3)C)C=CC=C2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.288 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (99.79 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.