Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

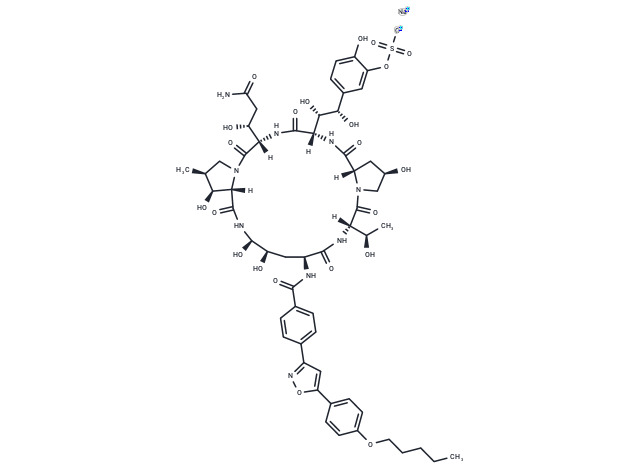
Micafungin sodium (FK 463) is the sodium salt form of micafungin, a semi-synthetic echinocandin derived from a natural product of the fungus Coleophoma empetri with antifungal activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $63 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $107 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $216 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $347 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $553 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,220 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $153 | In Stock |
| Description | Micafungin sodium (FK 463) is the sodium salt form of micafungin, a semi-synthetic echinocandin derived from a natural product of the fungus Coleophoma empetri with antifungal activity. |
| In vitro | Micafungin (10 mg/mL) effectively inhibits biofilm formation in the majority of examined isolates and significantly reduces mRNA transcription levels across all tested genes compared to untreated samples[1]. Additionally, when combined with KB425796-C, micafungin exhibits a fungicidal effect, significantly diminishing the colony-forming unit (CFU) count, unlike the fungistatic outcome (no CFU reduction) observed when either drug is applied independently[2]. |
| In vivo | Micafungin administration at a dose of 1 mg/kg notably extends survival in mice compared to those receiving saline. Additionally, a regimen combining micafungin (0.1 mg/kg) with KB425796-C (32 mg/kg) appears to enhance survival duration when compared to treatment with only micafungin (0.1 mg/kg). Treatment with micafungin alone reduces colony-forming units (CFUs) in the liver, though its clearance efficacy is not as pronounced as in the kidney. Significantly, a combined treatment of micafungin and KB425796-C markedly lowers CFU counts across all tested doses compared to micafungin treatment alone, demonstrating a superior clearance effect than that seen with AMPH-treated animals[2]. |
| Kinase Assay | HEK-GPR119 cells are transfected with GloSensor 22F plasmid and used for dynamic cAMP measurements 24-30 h later. Cell suspensions are made by dislodging the cells using PBS wash and Accutase treatment followed by resuspension in culture media. Cells are then washed twice by pelleting through centrifugation (300 g, 5 min) and resuspension in assay buffer (Hank's Balanced Salt Solution supplemented with 20 mM HEPES and 0.01% fatty acid free BSA, pH 7.4). Cells are then counted and diluted to 600,000 cells/mL in buffer, before GloSensor cAMP reagent is added (2% v/v) and equilibrated with the cells for 2 h at 20°C with periodic mixing. 50 μl/well of cells are added to white-bottomed 384 well plates (30,000 cells/well) in triplicate and baseline luminescence is measuring using an Envision plate-reader. 5 μL of MBX-2982 (serially diluted in DMSO and then diluted 1:100 in assay buffer to obtain ×10 concentrated solution) is manually added to the assay wells to achieve the stated final concentration. Plates are incubated at 20°C with luminescence read at regular intervals to detect dynamic cAMP changes over time within the same wells. cAMP responses at each time-point are expressed as fold over control (vehicle-treated cells)[1]. |
| Cell Research | Each fungal isolate is incubated statically in yeast-maltose (YM) agar broth for 24?h at 30°C.?Cryptococcus neoformans?YC203 is grown in YM broth medium for 20?h at 30°C with shaking at 200?r.p.m. A cell suspension is prepared by washing the cultured cells once with sterile saline.?A. fumigatus?FP1305 is cultured on a potato dextrose agar (PDA) slant for 4 days, and spores are then harvested in sterile saline and collected by filtering through gauze. Antifungal activity against all isolates, with the exception of C. neoformans, is measured by the micro-broth dilution method in 96-well culture plates using RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with?l-glutamine, but without sodium bicarbonate, and buffered to pH 7.0 with 0.165?m?MOPS. ForC. neoformans, yeast nitrogen base-glucose (YNBD) medium is used. For the assay, the test microorganism is inoculated into each well to yield 1×105?CFU/well, and the plates are then incubated for 20?h or 48?h at 37°C. Two end points are determined by microscopic observation: MEC, which is defined as a substantial reduction in fungal growth, and MIC, which is defined as a complete inhibition of growth. |
| Alias | Mycamine Sodium, FK463 Sodium, FK 463 |
| Molecular Weight | 1292.26 |
| Formula | C56H70N9NaO23S |
| Cas No. | 208538-73-2 |
| Smiles | [Na+].[H][C@@]12C[C@@H](O)CN1C(=O)[C@@]([H])(NC(=O)[C@H](C[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)NC(=O)[C@]1([H])[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C)CN1C(=O)[C@@]([H])(NC(=O)[C@@]([H])(NC2=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)c1ccc(O)c(OS([O-])(=O)=O)c1)[C@H](O)CC(N)=O)NC(=O)c1ccc(cc1)-c1cc(on1)-c1ccc(OCCCCC)cc1)[C@@H](C)O |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 45 mg/mL (34.82 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 100 mg/mL (77.38 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.