Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

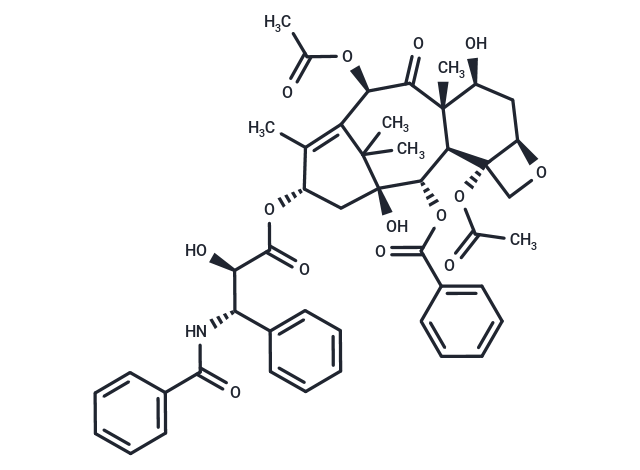
Paclitaxel (Taxol) is a natural product and a microtubule polymer stabilizer. Paclitaxel has anti-tumor activity and causes cell death by inducing mitotic arrest, apoptosis, and cell autophagy.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $34 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $48 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $78 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $118 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $173 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Paclitaxel (Taxol) is a natural product and a microtubule polymer stabilizer. Paclitaxel has anti-tumor activity and causes cell death by inducing mitotic arrest, apoptosis, and cell autophagy. |
| Targets&IC50 | Microtubule:4 nM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia cells CCRF-HSB-2 were treated with Paclitaxel (0.01-1 µM) for 48 h. Cell growth inhibition was detected by MTT. RESULTS: Paclitaxel dose-dependently inhibited the growth of CCRF-HSB-2 cells with an IC50 of 0.25 µM.[1] METHODS: Human gastric cancer cells AGS were treated with Paclitaxel (10-160 nM) for 24-48 h. The expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Paclitaxel induced the up-regulation of the expression of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP, which are apoptosis-related proteins. [2] METHODS: Canine mammary tumor cells CHMm were treated with Paclitaxel (0.01-1 μM) for 24 h. Apoptosis was detected using Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: Paclitaxel dose-dependently induced apoptosis in CHMm cells. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To investigate the effect of low-dose Paclitaxel on tumor invasion, Paclitaxel (2.6 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to SCID mice bearing cholangiocarcinoma tumor EGI-1 once daily for two weeks. RESULTS: Low-dose Paclitaxel treatment reduced the pulmonary spread of EGI-1 cells without significantly affecting their local tumor growth. [4] METHODS: To develop a preclinical model of Paclitaxel alcohol-induced negative affective symptoms, Paclitaxel (2-8 mg/kg in 1 volume ethanol+1 volume Emulphor-620 +18 volumes distilled water) was injected intraperitoneally into C57BL/6J mice every four injections were given to C57BL/6J mice once every two days. RESULTS: 8 mg/kg Paclitaxel treatment resulted in the development and maintenance of mechanical and cold abnormalities of pain. Paclitaxel also induced anxiety-like and depressive-like behaviors. Paclitaxel produced behavioral changes in the mouse affective state modeling assay, whereas the increase in injurious responses lasted longer. [5] |
| Kinase Assay | To determine which caspases are involved in apoptosis induced by taxol, caspase-3 inhibitor (DEVD-CHO), caspase-6 inhibitor (Z-VEID-FMK), caspase-8 inhibitor (Z-IETD-FMK or IETD-CHO), caspase-9 inhibitors (Z-LEHD-FMK or LEHD-CHO), and caspase-10 inhibitor (Z-AEVD-FMK) are used. These caspase inhibitors are dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (Me2SO); the final concentration of Me2SO is 0.1%. Cells (5×105) are preincubated in the presence or absence of 100 μM?each of these inhibitors for 3 h at 37°C then treated with or without 0.1, 0.5, and 1 μM?Paclitaxel for 48 h and processed for annexin V binding assay [1]. |
| Cell Research | 1×10^4 cells are plated in 100 μL of the growth medium in the presence or absence of increasing concentrations (0.1-1 μM) of taxol in 96-well plates and cultured at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 12-48 h. The cells are then incubated with 25 μL of MTT (5 mg/mL) at 37°C for 4 h. After dissolving the crystals with 0.04 N HCl in isopropanol, the plates are read in a microplate reader at 570 nm [1]. |
| Animal Research | Adult (250-320 g) male Sprague-Dawley rats are used for all experiments. One week following the DiI injection, rats are anesthetized with isofluorane and injected into the tail vein with 2 mg/kg paclitaxel or its vehicle (1:1:23, cremophor EL:ethanol:0.9% saline). The tail vein injection is repeated three more times every other day for a total of four injections [4]. |
| Alias | Taxol, NSC 125973 |
| Molecular Weight | 853.91 |
| Formula | C47H51NO14 |
| Cas No. | 33069-62-4 |
| Smiles | CC(=O)O[C@@H]1C2=C(C)[C@H](C[C@@](O)([C@@H](OC(=O)c3ccccc3)[C@@H]3[C@@]4(CO[C@@H]4C[C@H](O)[C@@]3(C)C1=O)OC(C)=O)C2(C)C)OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](NC(=O)c1ccccc1)c1ccccc1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.39g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 21.4 mg/mL (25.06 mM), Sonication is recommended. 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 8.54 mg/mL (10 mM), suspension.In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. DMSO: 41.66 mg/mL (48.79 mM), Heating is recommended. | ||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| |||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.