Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

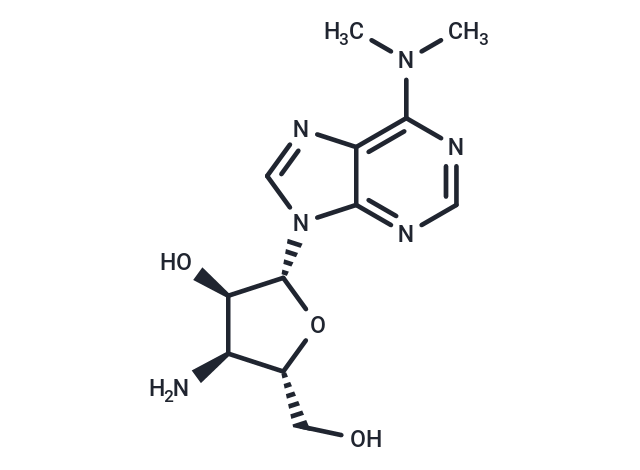
Puromycin aminonucleoside (NSC-3056) increases podocyte permeability by modulating ZO-1 in an oxidative stress-dependent manner.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $39 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $51 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $80 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $121 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $43 | In Stock |
| Description | Puromycin aminonucleoside (NSC-3056) increases podocyte permeability by modulating ZO-1 in an oxidative stress-dependent manner. |
| In vitro | Puromycin aminonucleoside -induced podocyte apoptosis is p53 dependent. Puromycin aminonucleoside causes podocyte apoptosis in a time-dependent manner. The IC50 values for PMAT-expressing and vector-transfected cells are 48.9 and 122.1 μM, respectively, suggesting expression of PMAT-enhanced cell sensitivity to Puromycin aminonucleoside. Puromycin aminonucleoside uptake in PMAT-expressing cells is fourfold higher at pH 6.6 than that at pH 7.4. Puromycin aminonucleoside (30 μg/mL) markedly enhances p53 protein levels in podocytes. Puromycin aminonucleoside (250 μM) is toxic to both PMAT-expressing and vector-transfected cells [2][4]. |
| In vivo | Rats administered Puromycin aminonucleoside (100 mg/kg, s.c.) exhibited reduced weight gain and elevated serum creatinine levels compared to controls. The podocyte count per glomerulus in control rats stood at 95.5±17.6, dropping to 90.7 by Day 4 in rats with Puromycin aminonucleoside (8 mg/100 g, i.v.)-induced nephrosis. Furthermore, nephrin levels per glomerulus in controls were 1.02±0.11 fmol, which decreased significantly in nephrosis rats to 0.46±0.06 fmol and 0.35±0.04 fmol on Days 4 and 7, respectively. This reduction in nephrin per podocyte was closely linked to proteinuria development in rats affected by Puromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis [5][6]. |
| Alias | NSC 3056 |
| Molecular Weight | 294.31 |
| Formula | C12H18N6O3 |
| Cas No. | 58-60-6 |
| Smiles | CN(C)c1ncnc2n(cnc12)[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](N)[C@H]1O |
| Relative Density. | 1.7 g/cm3 |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 33.33 mg/mL (113.25 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 31 mg/mL (105.33 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.