Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

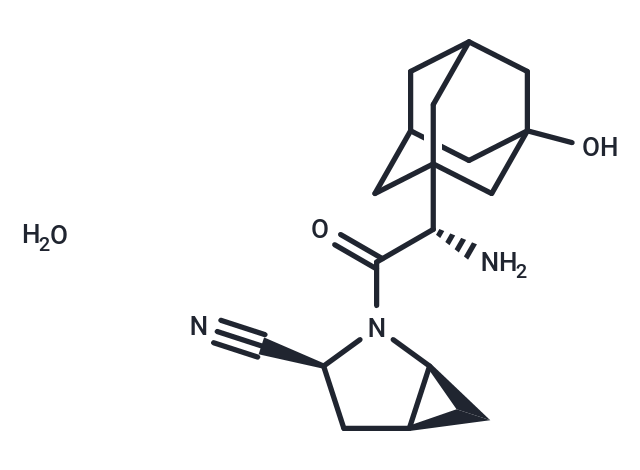
Saxagliptin hydrate (Onglyza hydrate) is a selective and reversible DPP4 inhibitor (IC50: 26 nM; Ki: 1.3 nM).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $40 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $56 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $93 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $143 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $213 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $533 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $39 | In Stock |
| Description | Saxagliptin hydrate (Onglyza hydrate) is a selective and reversible DPP4 inhibitor (IC50: 26 nM; Ki: 1.3 nM). |
| Targets&IC50 | DPP4:26 nM |
| In vitro | In vitro, saxagliptin inhibits FBS-, insulin- and IGF1-induced ERK phosphorylation and cell proliferation, in both MSC and MC3T3E1 preosteoblasts. In the absence of growth factors, saxagliptin has no effect on ERK activation or cell proliferation. In both MSC and MC3T3E1 cells, saxagliptin in the presence of FBS inhibits Runx2 and osteocalcin expression, type-1 collagen production and mineralization, while increasing PPAR-gamma expression[4]. |
| In vivo | Saxagliptin exerts direct beneficial effects on the arterial wall in an animal model of type 2 diabetes by increasing NO availability and improving antioxidant status. Saxagliptin reverses vascular hypertrophic remodeling and ameliorates NO availability in small arteries from db/db mice through the abrogation of NAD(P)H oxidase-driven eNOS uncoupling and by reducing the action of cyclooxygenase-1-derived vasoconstrictors downregulating the expression of thromboxane-prostanoid receptors[2]. DPP-4 inhibition with saxagliptin also improves pancreatic β-cell function in postprandial and fasting states, and decreases postprandial glucagon concentration[3]. |
| Cell Research | Sub-confluent cells are serum-starved overnight and then incubated with 1.5 or 15 μM saxagliptin and/or FBS (1%), insulin (5 ng/mL) or IGF1 (10-8 M) for 24 h (effects on cell proliferation) or 1 h (effects on signal transduction mechanisms). (Only for Reference) |
| Alias | Onglyza hydrate, BMS-477118 hydrate |
| Molecular Weight | 333.43 |
| Formula | C18H25N3O2·H2O |
| Cas No. | 945667-22-1 |
| Smiles | O.N[C@H](C(=O)N1[C@H]2C[C@H]2C[C@H]1C#N)C12CC3CC(CC(O)(C3)C1)C2 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 70 mg/mL (209.94 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 1 mg/mL (3 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 61 mg/mL (182.95 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/Ethanol/DMSO
Ethanol/DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.