Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Sitagliptin (MK0431), a new oral hypoglycemic (anti-diabetic drug), is a new dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor. This enzyme-inhibiting drug is used either alone or in combination with metformin or thiazolidinedione for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The drug can competitively inhibit a protein/enzyme and DPP-4, that leads to an incremental amount of active incretins (GLP-1 and GIP), the diminished amount of release of glucagon and increased release of insulin.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $36 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $50 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $59 | In Stock |
| Description | Sitagliptin (MK0431), a new oral hypoglycemic (anti-diabetic drug), is a new dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor. This enzyme-inhibiting drug is used either alone or in combination with metformin or thiazolidinedione for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The drug can competitively inhibit a protein/enzyme and DPP-4, that leads to an incremental amount of active incretins (GLP-1 and GIP), the diminished amount of release of glucagon and increased release of insulin. |
| Targets&IC50 | DPP4:18 nM |
| In vitro | Sitagliptin phosphate demonstrates a potent inhibitory effect on dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), achieving an IC50 of 19 nM in Caco-2 cell extracts[1]. It also inhibits in vitro migration of isolated splenic CD4 T-cells through cAMP/PKA/Rac1 pathway activation[2]. Furthermore, sitagliptin directly enhances GLP-1 secretion from intestinal L cells via a pathway that is independent of DPP-4, but relies on protein kinase A and MEK-ERK1/2 activation. Additionally, it mitigates the impact of autoimmunity on graft survival[3]. |
| In vivo | In vivo studies demonstrate that the ED50 (effective dose for 50% of the population) of sitagliptin phosphate, which inhibits DPP-4 activity in plasma, is estimated to be 2.3 mg/kg seven hours post-administration and 30 mg/kg twenty-four hours post-administration in freely fed Han-Wistar rats[1]. In the streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes mouse model, characterized by elevated plasma DPP-4 levels, sitagliptin phosphate supplementation notably reduces these levels, effectively regulating hyperglycemia and potentially enhancing islet graft longevity[4]. Moreover, pharmacokinetic profiles reveal that both plasma clearance and the volume of distribution for sitagliptin phosphate are significantly higher in rats (40-48 mL/min/kg, 7-9 L/kg) compared to dogs (9 mL/min/kg, 3 L/kg), with a half-life of 2 hours in rats versus 4 hours in dogs[5]. |
| Kinase Assay | DPP-4 is extracted from confluent Caco-2 cells. After 5 minutes of incubation at room temperature with lysis buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 0.04 U/mL aprotinin, 0.5% Nonidet P40, pH 8.0), cells are centrifuged at 35,000 g at 4°C for 30 minutes, and the supernatant is stored at -80°C. Assays are performed by mixing 20 μL of appropriate compound dilutions with 50 μL of the substrate for the DPP-4 enzyme, H-Ala-Pro-7-amido-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin (final concentration in the assay, 100 μM) and 30 μL of the Caco-2 cell extract (diluted 1000-fold with 100 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, pH 7.8). Plates are incubated at room temperature for 1 hour, and fluorescence is measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 405/535 nm using a SpectraMax GeminiXS. Dissociation kinetics of inhibitors from the DPP-4 enzyme is determined after a 1-hour preincubation of Caco-2 cell extracts with high inhibitor concentrations (30 nM for BI 1356, 3 μM for vildagliptin). The enzymatic reaction is started by adding the substrate H-Ala-Pro-7-amido-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin after a 3000-fold dilution of the preincubation mixture with assay buffer. Under these conditions, the difference in DPP-4 activity at a certain time point in the presence or absence of an inhibitor reflects the amount of this inhibitor still bound to the DPP-4 enzyme. Maximal reaction rates (fluorescence units/seconds ×1000) at 10-minute intervals are calculated using the SoftMax software of the SpectraMax and corrected for the rate of an uninhibited reaction [(vcontrol-vinhibitor)/vcontrol]. |
| Cell Research | CD4T-cells are plated on membrane inserts in serum-free RPMI 1640, and cell migration is assayed using Transwell chambers (Corning), in the presence or absence of purified porcine kidney DPP-4 (32.1 units/mg; 100 mU/mL final concentration) and DPP-4 inhibitor (100 μM). After 1 hour, cells on the upper surface are removed mechanically, and cells that have migrated into the lower compartment are counted. The extent of migration is expressed relative to the control sample. |
| Alias | MK0431 |
| Molecular Weight | 407.31 |
| Formula | C16H15F6N5O |
| Cas No. | 486460-32-6 |
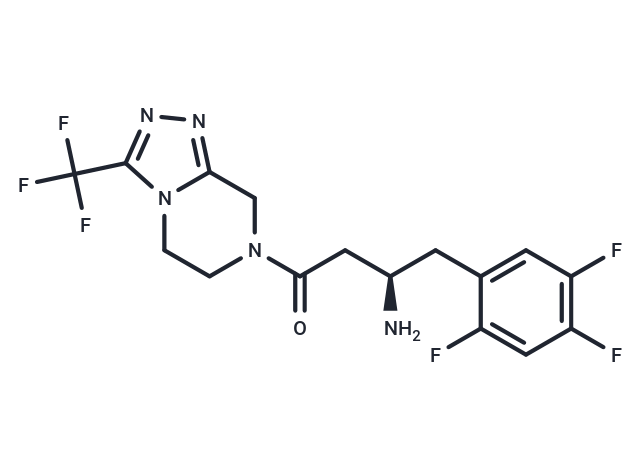
| Smiles | N[C@@H](CC(=O)N1CCn2c(C1)nnc2C(F)(F)F)Cc1cc(F)c(F)cc1F |
| Relative Density. | 1.614g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 16.67 mg/mL (40.93 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: <1 mg/mL (Insoluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.