Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

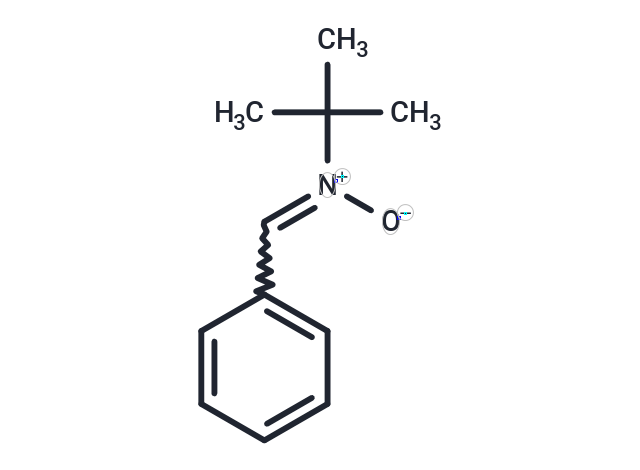
N-tert-butyl-α-Phenylnitrone ((Z)-N-benzylidene-2-Methylpropan-2-aMine oxide) inhibits COX2 catalytic activity. N-tert-butyl-α-Phenylnitrone((Z)-N-benzylidene-2-Methylpropan-2-aMine oxide) possesses potent reactive oxygen species scavenging, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-aging, and anti-diabetic activities, and can penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $37 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $52 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $78 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | N-tert-butyl-α-Phenylnitrone ((Z)-N-benzylidene-2-Methylpropan-2-aMine oxide) inhibits COX2 catalytic activity. N-tert-butyl-α-Phenylnitrone((Z)-N-benzylidene-2-Methylpropan-2-aMine oxide) possesses potent reactive oxygen species scavenging, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-aging, and anti-diabetic activities, and can penetrate the blood-brain barrier. |
| In vitro | Treatment of 25-100 μM N-tert-butyl-α-Phenylnitrone significantly reduces 2,2'-azobis (2-amidinopropane) dihydrochloride (AAPH)-induced intracellular ROS accumulation. N-tert-butyl-α-Phenylnitrone also attenuates AAPH-induced cytotoxicity, matrix degradation, and apoptosis, inhibiting AAPH-induced ERK/MAPK pathway activation[1]. |
| In vivo | In C57Bl/6 mice induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), intraperitoneal injection of 100 mg/kg N-tert-butyl-α-Phenylnitrone twice a day (on gestational day 8) abolishes LPS-induced lipid peroxidation, nitrate tyrosine residue levels and GSH depletion, and reduces the incidence of external malformations[2]. |
| Alias | (Z)-N-benzylidene-2-Methylpropan-2-aMine oxide |
| Molecular Weight | 177.24 |
| Formula | C11H15NO |
| Cas No. | 3376-24-7 |
| Smiles | CC(C)(C)[N+]([O-])=CC1=CC=CC=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 0.990 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (282.1 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.