Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Osalmid (Oxaphenamide) is a choleretic drug, inhibits ribonucleotide reductase activity by targeting ribonucleotide reductase small subunit M2 (RRM2).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $42 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $59 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $139 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $198 | In Stock |
| Description | Osalmid (Oxaphenamide) is a choleretic drug, inhibits ribonucleotide reductase activity by targeting ribonucleotide reductase small subunit M2 (RRM2). |
| Targets&IC50 | RRM2:8.23 μM |
| In vitro | Osalmid has been identified as a potential compound targeting the ribonucleotide reductase small subunit M2 (RRM2), exhibiting a tenfold higher efficacy in inhibiting ribonucleotide reductase (RR) activity than hydroxyurea. It significantly suppresses both HBV DNA and cccDNA synthesis within HepG2.2.15 cells, following a time- and dose-dependent manner. The effective concentration (EC50) for inhibiting HBV DNA is noted as 11.1 μM in culture supernatant and 16.5 μM in cells, following an 8-day treatment with Osalmid, which demonstrates a concentration-dependent suppression of RR activity, marked by an IC50 of 8.23 μM. Moreover, Osalmid has demonstrated potent activity against a 3TC-resistant HBV strain, indicating its potential in treating drug-resistant HBV infections[1]. |
| In vivo | Osalmid diminishes ribonucleotide reductase (RR) activity and hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication in HBV-transgenic mice, demonstrating synergistic effectiveness with lamivudine (3TC) while maintaining a low toxicity profile. Administered orally at a dosage of 400 mg/kg/day, osalmid progressively inhibits HBV DNA replication over time. A four-week treatment regimen results in a 40-45% decrease in HBV DNA replication levels in both the sera and liver tissues of mice, in comparison to untreated controls[1]. |
| Cell Research | HepG2.2.15 cells are cultured in the presence of 200 μg/mL G418. Cell viability is determined using a Cell Counting Kit-8 in 96-well plates treated with Osalmid for designated times. For long term assays, the culture supernatants are replaced with fresh media containing Osalmid every two days. The control wells contained equivalent amounts of DMSO. The CC50 is calculated as the concentration of a compound that reduced the cell viability to 50% compared to the control[1]. |
| Alias | Oxaphenamide, 4'-Hydroxysalicylanilide |
| Molecular Weight | 229.23 |
| Formula | C13H11NO3 |
| Cas No. | 526-18-1 |
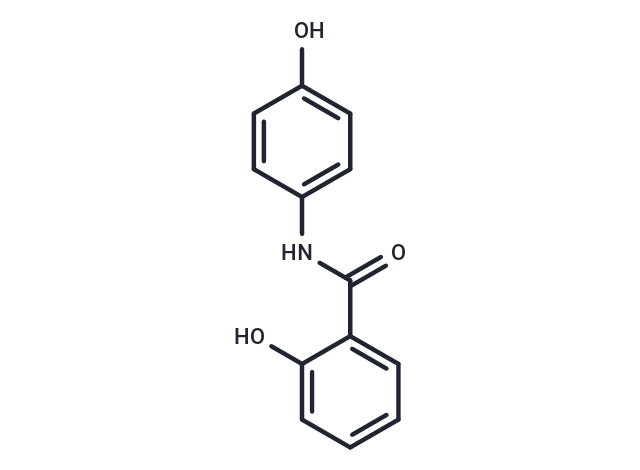
| Smiles | OC1=CC=C(NC(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2O)C=C1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.2084 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (218.12 mM) Ethanol: 41 mg/mL (178.9 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.