Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

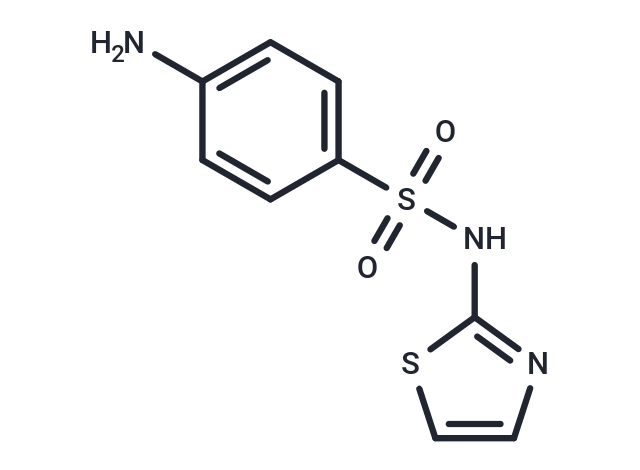
Sulfathiazole (2-Sulfanilamidothiazole), an organosulfur compound, has been served as a short-acting sulfa medicine.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $35 | In Stock | |
| 5 g | $81 | In Stock | |
| 10 g | $118 | In Stock |
| Description | Sulfathiazole (2-Sulfanilamidothiazole), an organosulfur compound, has been served as a short-acting sulfa medicine. |
| In vitro | Sulfathiazole (20 μg/L) begins degrading between days 31 and 38 in one of two batch reactors with different wastewater matrices, at a faster rate than sulfamethoxazole or sulfamethazine in the nitrification process (S3). [1] Recovery from spiked manure slurry samples is 64% for Sulfathiazole at pH 9. Sulfathiazole, with a pKa of 7.1 and retention times (tR) of 7.8, shows S/N values above 100 at the 1 mg/kg level. [2] Its sorption to inorganic sorbents is pH-dependent, influenced by sorbate speciation and sorbent charge properties, with cations being most significant for clay mineral sorption, followed by neutral species. [3] Sulfathiazole possesses at least five polymorphic forms: I, II, III, IV, and V and exists in the solid state in the imido form. [4] Sulfathiazole (94.9 mg/L) significantly increases reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and lipid peroxidation under ultraviolet B (UV-B) light exposure, upregulates alpha-esterase, hemoglobin, and vitellogenin mRNA, and significantly affects daphnid survival. [5] |
| Alias | 2-Sulfanilamidothiazole |
| Molecular Weight | 255.32 |
| Formula | C9H9N3O2S2 |
| Cas No. | 72-14-0 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (176.25 mM) Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.