Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Triparanol (NSC-65345) interferes with posttranslational modification of Hedgehog signaling molecules as well as the sterol sensing domain of its receptor PTCH1, leading to down-regulation of Hedgehog signaling. Triparanol suppresses human tumor growth and is an antilipemic agent with high ophthalmic toxicity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $298 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $678 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $912 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $1,350 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $1,790 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $2,470 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $726 | In Stock |
| Description | Triparanol (NSC-65345) interferes with posttranslational modification of Hedgehog signaling molecules as well as the sterol sensing domain of its receptor PTCH1, leading to down-regulation of Hedgehog signaling. Triparanol suppresses human tumor growth and is an antilipemic agent with high ophthalmic toxicity. |
| In vitro | Triparanol is an effective cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor blocking the 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase. Triparanol can block proliferation and induce apoptosis in multiple human cancer cells including lung, breast, liver, pancreatic, prostate cancer, and melanoma cells, and growth inhibition can be rescued by the exogenous addition of cholesterol[2]. |
| Alias | NSC-65345, NSC65345, NSC 65345, MER-29 |
| Molecular Weight | 438 |
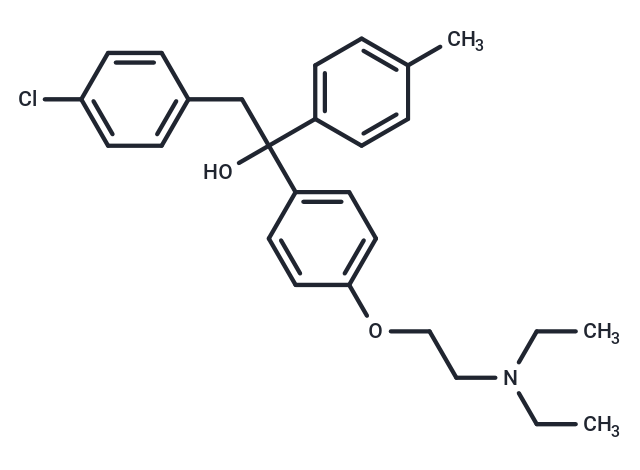
| Formula | C27H32ClNO2 |
| Cas No. | 78-41-1 |
| Smiles | C(CC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1)(O)(C2=CC=C(OCCN(CC)CC)C=C2)C3=CC=C(C)C=C3 |
| Relative Density. | 1.0173 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (114.16 mM) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.