Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

U0126-EtOH (U0126 Ethanol) is a non-ATP competitive specific inhibitor of MEK1/2 (IC50: 0.07/0.06 μM).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $65 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $78 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $98 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | U0126-EtOH (U0126 Ethanol) is a non-ATP competitive specific inhibitor of MEK1/2 (IC50: 0.07/0.06 μM). |
| Targets&IC50 | MEK2:60 nM (cell free), MEK1:70 nM (cell free) |
| In vitro | U0126 antagonized AP-1 transcriptional activity via noncompetitive inhibition of the dual specificity kinase MEK with an IC50 of 0.07 microM for MEK 1 and 0.06 microM for MEK 2 [1]. In fibroblasts treated with TPA/serum, U0126 suppressed the up-regulation of c-Fos and c-Jun proteins by 50–80%. Treatment with 10 μM U0126 did not affect the protein levels of the constitutively expressed transcription factors SP-1 or JunD and Fra-1 [2]. U0126 caused phosphorylation and activation of AMPK) and increased phosphorylation of its downstream target acetyl-CoA carboxylase, in HEK293 cells. This effect only occurred in cells expressing the upstream kinase, LKB1 [3]. |
| In vivo | Treatment of mice with U0126 via the aerosol route led to (i) inhibition of MEK activation in the lung (ii) reduction of progeny IAV titers compared to untreated controls (iii) protection of IAV infected mice against a 100× lethal viral challenge [4]. In all U0126 (10.5 mg/kg) experiments, engraftment and early tumor growth were significantly decreased. Furthermore, a 60–70% reduction in the volume of tumors treated with U0126 was obtained 9 days after injection and thereafter. Cdk1 expression was also strongly reduced in U0126-treated mice [5]. |
| Kinase Assay | The amount of immunoprecipitated wild type MEK used in these assays was adjusted to give a similar amount of activity units as obtained with 10 nM recombinant MEK. All other assays were performed with a recombinant, constitutively activated mutant MEK-1 (ΔN3-S218E/S222D) or constitutively active MEK-2(S222E/S226D). Reaction velocities were measured using a 96-well nitrocellulose filter apparatus as described below. Unless otherwise noted, reactions were carried out at an enzyme concentration of 10 nM, in 20 mM Hepes, 10 mM MgCl2, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 0.1 mg/ml BSA, pH 7.4, at room temperature. Reactions were initiated by the addition of [γ-33P]ATP into the premixed MEK/ERK/inhibitor reaction mixture, and an aliquot of 100 μl was taken every 6 min and transferred to the 96-well nitrocellulose membrane plate which had 50 mM EDTA to stop the reaction. The membrane plate was drawn and washed 4 times with buffer under vacuum. Wells were then filled with 30 μl of Microscint-20 scintillation fluid, and the radioactivity of33P-phosphorylated ERK was counted with a Top Count scintillation counter. Velocities were obtained from the slopes of radioactivity versus time plots. Concentrations of ERK and ATP were 400 nM and 40 μM, respectively, unless otherwise indicated [2]. |
| Cell Research | HEK293 cells were maintained in Dulbecco's modification of Eagle's medium (low glucose) plus 10% foetal bovine serum. HeLa cells stably expressing wild type or kinase-dead LKB1 have been described. AMPK activity was determined by immunoprecipitate kinase assays using anti-AMPK-a1 and -a2 antibodies. Antibodies recognising AMPK phosphorylated on Thr-172 (anti-pT172), AMPK-α1 and -α2 and acetyl-CoA carboxylase-1 (ACC1) phosphorylated on Ser-80 [16] were described previously. Quantification of ratios of signals from phosphorylated and total protein using these antibodies was performed by dual labelling using the LI-COR Odyssey IR imager as described. Contents of ATP and ADP were determined for cells in 6 cm culture dishes by quickly pouring off the medium, adding 350 μl of ice-cold 5% perchloric acid, scraping the cells off with a plastic scraper, and centrifuging (14 000 · g; 3 min, 4 °C) to remove insoluble material. The perchloric acid was then extracted from the supernatant and nucleotides analysed by capillary electrophoresis of perchloric acid extracts as described previously. All incubations of cells were performed in triplicate and results are expressed as means ± S.E.M [3]. |
| Animal Research | Prior to injection, FI cells were labeled with a stable fluorescent dye molecule, DiA at 10 μg/ml for 5 h at 37 1C. After washing to remove free DiA, cells were trypsinized for inoculation (U0126 experiments) or transfection (RNAi experiments). Biliary epithelial cells were injected subcutaneously, at the indicated times, into the tibia of nude mice. In the chemical experiments, 3h after inoculation, mice were treated with U0126 (10.5 mg/kg) daily by intraperitoneal injection. The length and width of each tumor were measured every day by using a caliper. The following formula was used to calculate tumor volumes ? width2 length/2. Mice were killed at the end of experiment. Tumors were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen [5]. |
| Alias | U0126 Ethanol, U0126 |
| Molecular Weight | 426.6 |
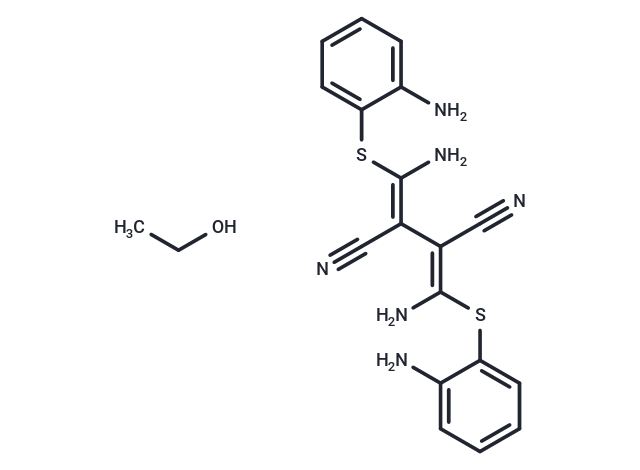
| Formula | C18H16N6S2·C2H6O |
| Cas No. | 1173097-76-1 |
| Smiles | CCO.N\C(Sc1ccccc1N)=C(\C#N)/C(/C#N)=C(\N)Sc1ccccc1N |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 7.9 mg/mL (18.52 mM), In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 55 mg/mL (128.93 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.