Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

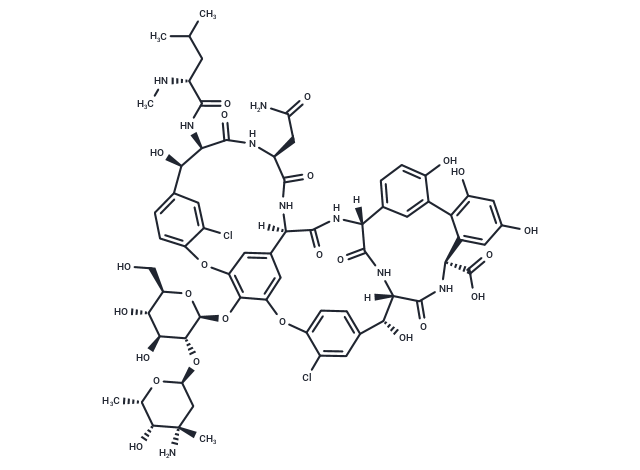
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic that exerts its antimicrobial activity by altering the permeability of cell membranes and selectively inhibiting ribonucleic acid synthesis. Vancomycin can be used for the treatment of serious infections for which all antibiotics have failed.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $42 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $66 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $98 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $298 | In Stock |
| Description | Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic that exerts its antimicrobial activity by altering the permeability of cell membranes and selectively inhibiting ribonucleic acid synthesis. Vancomycin can be used for the treatment of serious infections for which all antibiotics have failed. |
| In vitro | METHODS: B. burgdorferi was treated with Vancomycin (0.5-2.0 µg/mL) for 24 h and cell morphology was examined using real-time time-lapse microscopy. RESULTS: At higher concentrations of Vancomycin (≥1.0 µg/mL), many abnormal cells were observed, which were visually identified by vesiculation, granule formation, and morphological changes. The proportion of these abnormal bacteria in the population increased in a dose-dependent manner. [1] METHODS: Human osteosarcoma cells MG-63 were treated with Vancomycin (10-10000 µg/mL) for 24-72 h. Cell counts were measured using an Elzone Celi Counter. RESULTS: Localized levels of Vancomycin at 1000 µg/mL and below had little effect on osteoblast replication, and concentrations of 10,000 µg/mL resulted in cell death. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To detect nephrotoxicity, Vancomycin (400 mg/kg) and Vitamin C (200 mg/kg) were administered intraperitoneally to C57BL/6J mice once daily for seven days. RESULTS: Renal index, renal injury score, apoptosis, serum Cr and BUN, as well as renal Cr, BUN, MDA, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and NF-κB were higher in the Vancomycin group than in the control group, whereas body weight and renal SOD activity were lower. On the contrary, no differences were observed between the control and Vitamin C groups in all these indices. [3] METHODS: To deplete the intestinal microbiota of mice, the antibiotics (ABX) Vancomycin (0.5 g/L), Ampicillin (1 g/L), Neomycin sulfate (1 g/L), and metronidazole (1 g/L) were administered to mice by drinking water for two weeks. RESULTS: Antibiotics significantly reduced the diversity and composition of the gut microbiota. [4] |
| Molecular Weight | 1449.25 |
| Formula | C66H75Cl2N9O24 |
| Cas No. | 1404-90-6 |
| Smiles | O(C=1C2=CC3=CC1OC=4C(Cl)=CC(=CC4)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](NC([C@@H](CC(C)C)NC)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(N)=O)C(=O)N[C@]3(C(=O)N[C@@]5(C=6C=C(C=7C([C@@H](C(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@]([C@H](O)C=8C=C(Cl)C(O2)=CC8)(NC5=O)[H])=CC(O)=CC7O)C(O)=CC6)[H])[H])[C@H]9[C@H](O[C@H]%10C[C@](C)(N)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)O%10)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O9 |
| Relative Density. | 1.65 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Solubility Information | 10% DMSO+90% Saline: 1 mg/mL (0.69 mM), In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. DMSO: 50 mg/mL (34.5 mM), Sonication is recommended. |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.