Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

RITA (NSC-652287)(NSC-652287) induced cross-links of both DNA-DNA and DNA-protein with no detectable DNA single-strand breaks. RITA, like nutlin-3, can disrupt the p53/Mdm2 interaction.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $38 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $61 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $198 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $363 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $535 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $752 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,150 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $82 | In Stock |
| Description | RITA (NSC-652287)(NSC-652287) induced cross-links of both DNA-DNA and DNA-protein with no detectable DNA single-strand breaks. RITA, like nutlin-3, can disrupt the p53/Mdm2 interaction. |
| Targets&IC50 | p53dN:1.5 nM (Kd) |
| In vitro | RITA (10 nM) caused cell cycle arrest and accumulation of cells in the G2-M phase, and at 100 nM it induced DNA fragmentation and apoptosis and increased p53 protein levels. RITA (30 nM) also induced the production of DNA-protein and DNA-DNA crosslinks in A498 cells. At the same time, RITA did not affect top1-regulated superhelical SV40 DNA loosening. RITA significantly inhibited HCT116 cell growth (97%) and slightly inhibited HCT116 TP53-/- cell growth (13%). RITA inhibited the growth of wild-type p53-expressing cells more effectively than that of cells lacking p53 or with p53 mutation. When acting on tumor cells, RITA showed a high degree of selectivity for different toxicities due to the accumulation of cytoplasmic (S100) fractions.RITA bound to full-length p53 but not to glutathione S-transferase proteins or HDM-2.RITA also inhibited the growth of other renal cell lines including ACHN and UO-31 (IC50: 13 μM and 37 μM). RITA blocked p53-HDM-2 interaction and p53 ubiquitination.RITA caused a significant decrease in the amount of HDM-2 co-precipitated with p53, although both proteins were up-regulated.RITA blocked the interaction between 6XHis-tagged His-HDM-2 protein and purified GST-p53. By promoting p53Ser46 phosphorylation, RITA induces apoptosis. RITA induced p53 activation and showed upregulation of phosphorylated MKK-4, ASK-1 and c-Jun. It also induced JNK signaling activation. NMR results showed that RITA did not block the formation of the complex between the N-terminal p53-binding domain (residues 1-118) and p53 (residues 1-312) of MDM2, which may be related to the fact that the binding of RITA requires the natural conformation of p53. |
| In vivo | RITA (10 nM) caused cell cycle arrest and accumulation of cells in the G2-M phase, and at 100 nM it induced DNA fragmentation and apoptosis and increased p53 protein levels. RITA (30 nM) also induced the production of DNA-protein and DNA-DNA crosslinks in A498 cells. At the same time, RITA did not affect top1-regulated superhelical SV40 DNA loosening. RITA significantly inhibited HCT116 cell growth (97%) and slightly inhibited HCT116 TP53-/- cell growth (13%). RITA inhibited the growth of wild-type p53-expressing cells more effectively than that of cells lacking p53 or with p53 mutation. When acting on tumor cells, RITA showed a high degree of selectivity for different toxicities due to the accumulation of cytoplasmic (S100) fractions.RITA bound to full-length p53 but not to glutathione S-transferase proteins or HDM-2.RITA also inhibited the growth of other renal cell lines including ACHN and UO-31 (IC50: 13 μM and 37 μM). RITA blocked p53-HDM-2 interaction and p53 ubiquitination.RITA caused a significant decrease in the amount of HDM-2 co-precipitated with p53, although both proteins were up-regulated.RITA blocked the interaction between 6XHis-tagged His-HDM-2 protein and purified GST-p53. By promoting p53Ser46 phosphorylation, RITA induces apoptosis. RITA induced p53 activation and showed upregulation of phosphorylated MKK-4, ASK-1 and c-Jun. It also induced JNK signaling activation. NMR results showed that RITA did not block the formation of the complex between the N-terminal p53-binding domain (residues 1-118) and p53 (residues 1-312) of MDM2, which may be related to the fact that the binding of RITA requires the natural conformation of p53. |
| Kinase Assay | The inhibition profile of cabozantinib against a broad panel of 270 human kinases is determined using luciferase-coupled chemiluminescence,?33P-phosphoryl transfer, or AlphaScreen technology. Recombinant human full-length, glutathione?S-transferase tag, or histidine tag fusion proteins are used, and half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values are determined by measuring phosphorylation of peptide substrate poly (Glu, Tyr) at ATP concentrations at or below the?Km?for each respective kinase. The mechanism of kinase inhibition is evaluated using the AlphaScreen Assay by determining the IC50?values over a range of ATP concentrations. |
| Cell Research | Examination to assess susceptibility of cells to RITA (0.1 nM - 1 mM) is done using the XTT assay. Cells are inoculated into 96-well flat-bottom plates at a density of 1500 cells per well and incubated for 24 hours at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2 5% air atmosphere. Serial concentrations of RITA in DMSO are added to the wells, and sensitivity is determined 48 hours after the addition of RIT(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | RITA (NSC 652287), NSC 652287 |
| Molecular Weight | 292.37 |
| Formula | C14H12O3S2 |
| Cas No. | 213261-59-7 |
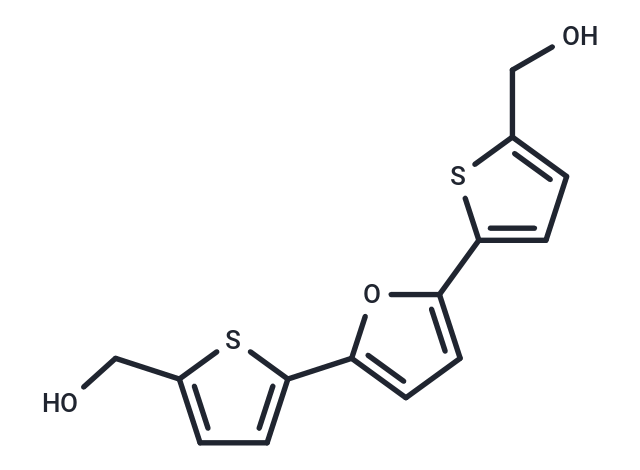
| Smiles | OCc1ccc(s1)-c1ccc(o1)-c1ccc(CO)s1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.396 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (153.91 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 7.3 mg/mL (24.97 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.