Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

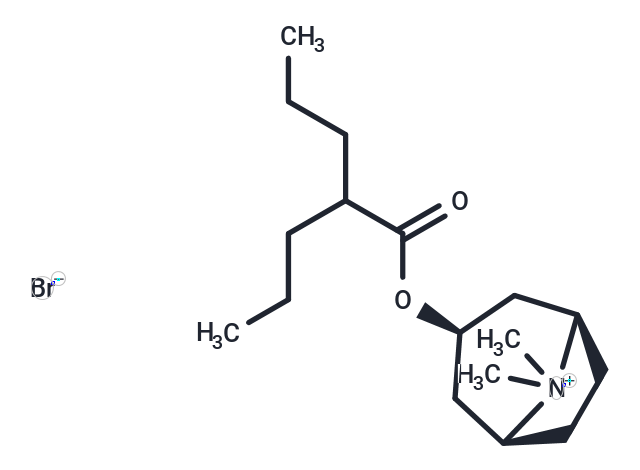
Anisotropine Methylbromide is an anticholinergic agent and has been used for relief of gastrointestinal spasm and for the suppression of gastric acid secretion.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | 28 € | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | 38 € | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | 57 € | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | 81 € | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | 117 € | In Stock |
| Description | Anisotropine Methylbromide is an anticholinergic agent and has been used for relief of gastrointestinal spasm and for the suppression of gastric acid secretion. |
| Targets&IC50 | IP:1.9 nM (EC50), DP1:0.6 nM (EC50), EP3:68.9 nM (EC50), EP2:6.2 nM (EC50) |
| In vitro | Treprostinil has a high affinity for the IP, EP2 and DP1 receptors (Ki: 32, 3.6 and 4.4 nM, respectively), low affinity for EP1 and EP4 receptors and even lower affinity for EP3, FP, and TP receptors. Activation of IP, DP1 and EP2 receptors can all result in vasodilatation of human pulmonary arteries[1]. Treprostinil inhibits the viability of cultured endothelial colony forming cells. Endothelial colony forming cells proliferation is stimulated by conditioned media from Treprostinil pretreated mesenchymal stem cells [2]. |
| In vivo | Treprostinil is most efficacious in raising intracellular cAMP levels in murine and human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells [2]. Treprostinil preserves the sinusoidal endothelial cell lining and reduces platelet deposition early post-transplantation compared to placebo. Hepatic tissue blood flow is significantly compromised in the placebo group, whereas treprostinil maintains blood flow similar to normal levels [3]. Treprostinil treatment significantly increases the vessel-forming ability of endothelial colony forming cells combined with mesenchymal stem cells in Matrigel implanted in nude mice. Silencing VEGF-A gene in mesenchymal stem cells also blocks the pro-angiogenic effect of Treprostinil [4]. Treatment with Treprostinil significantly reduces the recruitment of cells compared to normoxic mice. Treprostinil also reduces right ventricular systolic pressure and slightly reduces the vascular remodeling but fails to reverse the right ventricular hypertrophy [5]. |
| Cell Research | Human or murine hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells are incubated in the presence of vehicle or the combination of 10 μM Treprostinil and 30 μM forskolin at 37°C for 1 hour and 24 hours. After washing with phosphate-buffered saline at 4°C, cells are stained for externalized phosphatidylserine with the apoptosis kit [2]. |
| Animal Research | Male Lewis rats weighing 200-300 g are used in the study. Donor animals receive treprostinil or placebo 24 h before hepatectomy and the corresponding recipient animal receive a similar treatment until the time of sacrifice. The surgeon is blinded to treatment. Recipients are sacrificed at 1, 3, 6, 24 and 48 h post-transplantation to examine the early events after IRI. Treprostinil (100 ng/kg/min) or placebo is administered subcutaneously via an Alzet implantable osmotic pump. This dose is selected to achieve a steady-state plasma concentration in the range of 5-20 ng/mL [3]. . Bone marrow transplanted (BMT) mice are divided into five different groups with each group consisting of 6 to 10 mice. One group of mice is exposed to hypoxia (10% inspired oxygen fraction) in a normobaric chamber whereas the second group (control BMT) of animals are placed in a normoxic chamber with a normal oxygen environment (21% inspired O2 fraction) for 28 days. Sham group mice receive saline treatment whereas two other groups of mice receive Treprostinil infusions of different dose levels (14 ng/kg and 70 ng/kg per minute) and are exposed to hypoxia for 4 weeks. For comparison, human infusion rates in PAH therapy vary from 10 to 60 ng/kg per min[5]. |
| Molecular Weight | 362.35 |
| Formula | C17H32BrNO2 |
| Cas No. | 80-50-2 |
| Smiles | [Br-].CCCC(CCC)C(=O)O[C@@H]1C[C@@H]2CC[C@H](C1)[N+]2(C)C |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (137.99 mM) H2O: 198.7 mM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.