Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Calpeptin is a potent, cell-permeable calpain inhibitor.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $44 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $61 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $113 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $186 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $275 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $57 | In Stock |
| Description | Calpeptin is a potent, cell-permeable calpain inhibitor. |
| Targets&IC50 | Calpain I (porcine erythrocytes):52 nM(ID50), Papainb:138 nM(ID50), Calpain II (porcine kidney):34 nM(ID50), Calpain I (human platelets):40 nM(ID50) |
| In vitro | Calpeptin inhibits 20K phosphorylation in a dose-related manner in platelets stimulated by thrombin, ionomycin or collagen. [1] In differentiating PC12 cells, Calpeptin promotes neurite elongation via inhibition of Calpain activity. [2] In rat retinal ganglion cells, Calpeptin attenuates apoptosis, maintains normal whole-cell membrane potential, and thus provides functional neuroprotection. [3] |
| In vivo | In a feline right ventricular (RV) PO (RVPO) model, calpeptin (0.6 mg/kg, i.v.) blocks the activation of calpain and caspase-3, cleavage of their substrates, and cardiomyocyte programmed cell death. [4] In a rat focal cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury model, Calpeptin reduces the neuronal apoptosis in hippocampal CA1 sector via inhibition of the expression of Caspase-3. [5] |
| Molecular Weight | 362.46 |
| Formula | C20H30N2O4 |
| Cas No. | 117591-20-5 |
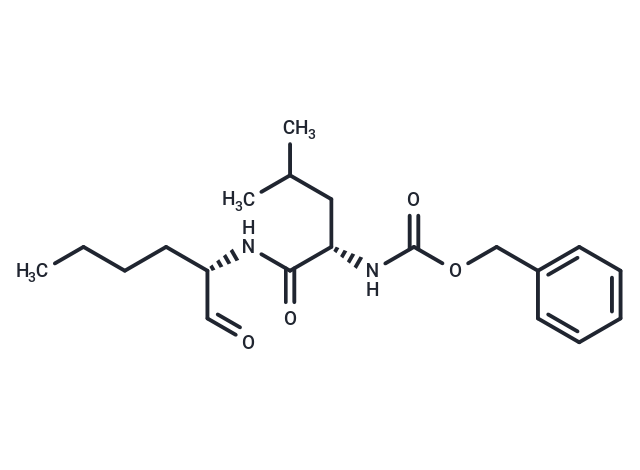
| Smiles | CCCC[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)OCc1ccccc1)C=O |
| Relative Density. | 1.1667 g/cm3 (Estimated) |
| Storage | store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 67 mg/mL (184.85 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 80 mg/mL (220.71 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.