Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

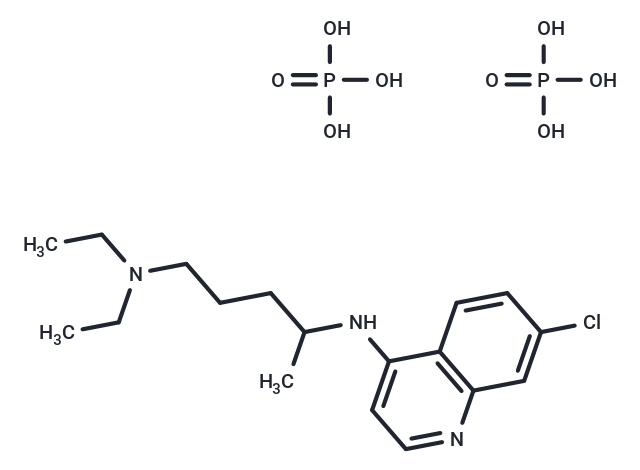
Chloroquine phosphate (Aralen phosphate) is an aminoquinoline antimalarial and also is widely used as an autophagy inhibitor. Chloroquine also is an inhibitor of toll-like receptors (TLRs).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $42 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $50 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $66 | In Stock |
| Description | Chloroquine phosphate (Aralen phosphate) is an aminoquinoline antimalarial and also is widely used as an autophagy inhibitor. Chloroquine also is an inhibitor of toll-like receptors (TLRs). |
| Targets&IC50 | Cytotoxicity against human K562 cells:31.83 nM, Cytotoxicity against hμMan KB cells by microplate method:0.6 μM |
| In vitro | Chloroquine (20 μM) inhibits IL-12p70 release and reduces Th1-priming capacity of activated human monocyte-derived Langerhans-like cells (MoLC). Chloroquine (20 μM) enhances IL-1–induced IL-23 secretion in MoLC and subsequently increases IL-17A release by primed CD4+ T cells [1]. Chloroquine (25 μM) suppresses MMP-9 mRNA expression in normoxia and hypoxia in parental MDA-MB-231 cells. Chloroquine has cell-, dose- and hypoxia-dependent effects on MMP-2, MMP-9 and MMP-13 mRNA expression [2]. TLR7 and TLR9 inhibition using chloroquine significantly reduce HuH7 cell proliferation in vitro [3]. |
| In vivo | Chloroquine (80 mg/kg, i.p.) fails to inhibit the proliferation of triple-negative MDA-MB-231 cells regardless of their high or low TLR9 expression levels in the orthotopic mouse model [2]. However, chloroquine's suppression of TLR7 and TLR9 significantly reduces tumor growth in the mouse xenograft model, and it likewise markedly impedes HCC development in the DEN/NMOR rat model [3]. |
| Cell Research | The cells are cultured in 6-well plates with normal culture medium in the presence of vehicle or 25 or 50 μM chloroquine, until near confluency, after which they are rinsed with sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and cultured further for the indicated times in serum-free culture medium. At the desired time-points, the culture medium is discarded and the cells are quickly harvested in lysis buffer and clarified by centrifugation. Subsequent to boiling the supernatants in reducing sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer, equal amounts of protein (100 μg) are loaded per lane and the samples are electrophoresed into 10 or 4-20% gradient polyacrylamide SDS gels, then transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. To detect TLR9, the blots were incubated overnight at 4°C with anti-TLR9 antibodies, diluted 1:500 in Tris-buffered saline with 0.1% (v/v) Tween-20 (TBST). Equal loading is confirmed with polyclonal rabbit anti-actin. Secondary detection is performed with horseradish peroxidase-linked secondary antibodies. The protein bands are visualized by chemiluminescence using an ECL kit [2]. |
| Animal Research | Control and TLR9 siRNA MDA-MB-231 cells (5×105 cells in 100 μL) are inoculated into the mammary fat pads of four-week-old, immune-deficient mice (athymic nude/nu Foxn1). Treatments are started seven days after tumor cell inoculation. The mice are treated daily either with intraperitoneal (i.p.) chloroquine (80 mg/kg) or vehicle (PBS). The animals are monitored daily for clinical signs. Tumor measurements are performed twice a week and tumor volume is calculated according to the formula V=(π/6) (d1×d2)3/2, where d1 and d2 are perpendicular tumor diameters. The tumors are allowed to grow for 22 days, at which point the mice are sacrificed and the tumors are dissected for a final measurement. Throughout the experiments, the animals are maintained under controlled pathogen-free environmental conditions (20-21°C, 30-60% relative humidity and a 12-h lighting cycle). The mice are fed with small-animal food pellets and supplied with sterile water ad libitum [2]. |
| Alias | Chloroquine diphosphate, Chingamin phosphate, Aralen phosphate |
| Molecular Weight | 515.87 |
| Formula | C18H26CLN3·2(H3PO4) |
| Cas No. | 50-63-5 |
| Smiles | OP(O)(O)=O.OP(O)(O)=O.CCN(CC)CCCC(C)NC1=CC=NC2=C1C=CC(Cl)=C2 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: Insoluble H2O: 10 mM, Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
H2O
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.