Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $34 | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $48 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $81 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $121 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $212 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $297 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $468 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,050 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $86 | In Stock |
| Description | PP1 (AGL 1872), a specific and effective Src inhibitor, is with IC50 for Lck/Fyn is 5 nM/ 6 nM, respectively. |
| Targets&IC50 | Fyn:6 nM, Lck:5 nM |
| In vitro | PP1 is a nano-molar inhibitor of Lck and FynT, inhibits anti-CD3-induced protein-tyrosine kinase activity in T cells (IC50, 0.5 μM), demonstrates selectivity for Lck and FynT over ZAP-70, and preferentially inhibits T cell receptor-dependent anti-CD3-induced T cell proliferation (IC50, 0. 5 μM) over non-T cell receptor-dependent phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate/interleu-kin-2 (IL-2)-induced T cell proliferation. PP1 (1 μM) selectively inhibits the induction of the IL-2 gene, but not the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor or IL-2 receptor genes. PP1 also inhibits Src (IC50, 170 nM) and Hck (IC50, 20 nM). PP1 is 50–100-fold less active in the inhibition of A-431 epidermal growth factor receptor autophosphorylation (IC50, 0.25 μM). [1] PP1 also inhibits Kit and Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinases with IC50 of ~75 nM and 1 μM, respectively. PP1 completely abrogates the proliferation of M07e cells in response to SCF with IC50 of 0.5–1 μM. PP1 (1 μM) inhibits SCF-induced c-Kit autophosphorylation in intact cells and blocks the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and Akt. PP1 inhibits the activity of mutant constitutively active forms of c-Kit (D814V and D814Y) found in mast cell disorders, and triggers apoptosis in the rat basophilic leukemia cell line RBL-2H3 that expresses mutant c-Kit. PP1 reduces the constitutive activation of signal transducer and activators of transcription 5 and mitogen-activated protein kinase and triggeres apoptosis in FDCP1 cells expressing Bcr-Abl. [2] |
| Kinase Assay | Protein A-Sepharose beads (prepared as a 50% (w/v) suspension) are added to the antibody/lysate mixture at 250 μL/mL and allowed to incubate for 30 min at 4°C. The beads are then washed twice in 1 mL of lysis buffer and twice in 1 mL of kinase buffer (25 mM HEPES, 3 mM MnCl2, 5 mM MgCl2, and 100 μM sodium orthovanadate) and resuspended to 50% (w/v) in kinase buffer. Twenty-five microliters of the bead suspension is added to each well of the enolase-coated 96-well high protein binding plate together with an appropriate concentration of compound and [γ-32P]ATP (25 μL/well of a 200 μCi/mL solution in kinase buffer). After incubation for 20 min at 20°C, 60 μL of boiling 2× solubilization buffer containing 10 mM ATP is added to the assay wells to terminate the reactions. Thirty microliters of the samples is removed from the wells, boiled for 5 min, and run on a 7.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. The gels are subsequently dried and exposed to Kodak X-AR film. For quantitation, films are scanned using a Molecular Dynamics laser scanner, and the optical density of the major substrate band, enolase p46, is determined. Concentrations of compound that causes 50% inhibition of enolase phosphorylation (IC50) are determined from a plot of the density versus concentration of compound. In companion experiments for measuring the activity of compounds against Lck, the assay plate is washed with two wash cycles on a Skatron harvester using 50 mM EDTA, 1 mM ATP. Scintillation fluid (100 μL) is then added to the wells, and P incorporation is measured using a Pharmacia Biotech micro-β-counter. Concentrations of compound that causes 50% inhibition of enzyme activity (IC50) are determined from a plot of the percent inhibition of enzyme activity versus concentration of compound[1]. |
| Cell Research | PP1 is dissolved in DMSO and stored, and then diluted with appropriate medium before use[2]. Inhibition of anti-CD3-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation in purified human peripheral blood T cells is measured as follows. All incubations are carried out at 37°C in an Eppendorf Thermomixer 5436 at a mixing setting of 11. Cells (1×106 in 100 μL of RPMI 1640 medium) are incubated for 15 min with drug prior to a 6-min incubation with 1 μg of anti-CD3/mL (anti-leu4, 100 μg/mL). The final volume of the reaction is 115 μL. Reactions are terminated by the addition of 57.5 μL of 3× solubilization buffer incubated at 100°C prior to its addition. Samples are mixed, boiled for 5 min, and stored at -70°C. Western blots of these cell lysates, run on 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gels, are probed with a polyclonal anti-phosphotyrosine antibody, and immune complexes are detected with I-labeled protein A (ICN). For quantitation, films are scanned using a Molecular Dynamics laser scanner, and the optical densities of the major substrate band, p70, are quantitated in the presence of anti-CD3 (in the presence and absence of drug). Percent inhibition is calculated as follows: (1-(p70 optical density units in presence of drug/p70 units in absence of drug))×100. IC50 equals the concentration of compound at which 50% inhibition is measured[1]. |
| Alias | EI 275, AGL 1872 |
| Molecular Weight | 281.36 |
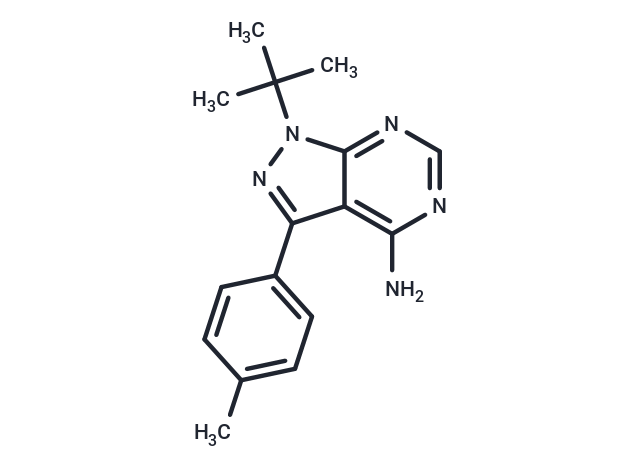
| Formula | C16H19N5 |
| Cas No. | 172889-26-8 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 4 mg/mL (14.21 mM) Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.