Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

UM-164 (DAS-DFGO-II), a highly potent c-Src inhibitor with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 2.7 nM, also effectively inhibits p38α and p38β.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $43 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $68 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $122 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $198 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $297 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $439 | In Stock |
| Description | UM-164 (DAS-DFGO-II), a highly potent c-Src inhibitor with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 2.7 nM, also effectively inhibits p38α and p38β. |
| Targets&IC50 | c-Src:2.7 nM |
| In vitro | UM-164 is an effective inhibitor of c-Src, showing a binding potency close to that of Dasatinib (UM-164 Kd=2.7 nM, Dasatinib Kd=0.7 nM) in biochemical assays. Its capability to inhibit c-Src activation was assessed through its effect on c-Src autophosphorylation in MDA-MB 231 and SUM 149 TNBC cell lines, revealing concentration- and time-dependent inhibition. Notably, at 120 minutes and a concentration of 50 nM, UM-164 completely abrogated c-Src autophosphorylation, confirming its potent inhibitory action in vitro. Additionally, flow cytometry experiments indicated that UM-164 treatment increased the proportion of G0-G1 cells by 25% and 28% in MDA-MB 231 and SUM 149 cells respectively, while simultaneously decreasing the S cell fraction by 16% and 19%, respectively[1]. |
| In vivo | In a xenograft study, NCr/nude mice implanted with MDA-MB 231 and SUM 149 cell lines are observed. Once tumors are palpable, mice are divided into control and treatment groups, receiving intraperitoneal injections of either the drug (doses of 10 and 20 mg/kg for both cell types, with an additional 15 mg/kg for SUM 149) or a vehicle bi-daily (n=5 per group). Following treatment with UM-164 at selected doses, no noteworthy adverse effects like weight loss or abnormalities are evident in treated mice even after 52 days. Importantly, tumor growth is significantly reduced in both 10 and 20 mg/kg dosage groups compared to the vehicle group (P<0.026 and P<0.004, respectively)[1], demonstrating the compound's efficacy. |
| Cell Research | MDA-MB 231 and SUM 149 cells are plated in triplicate on 60 mm dishes at a density of 1×106 cells/flask. After 24 h, a final concentration of 1 μM UM-164 is added to the cells and incubated for 24 h. Growth medium is then removed and cells are washed with PBS. The remaining cells are trypsinized, harvested, and placed together with growth medium and PBS. Cells are pelleted and re-suspended in 3 mL of 75% ethanol, followed by overnight storage at - 20°C. After incubation, cells are centrifuged at 1,500 rpm for 5 min and the cell pellets are re-suspended in 0.05 mg/mL propidium iodide (10 μg/mL) containing 300 μg/mL RNase. Cell clumps are filtered. Cell DNA content is measured on flow cytometer and cell cycle distribution is calculated from 10,000 cells using FACS analysis[1] . |
| Animal Research | Mice[1] |
| Alias | UM164, DAS-DFGO-II |
| Molecular Weight | 640.68 |
| Formula | C30H31F3N8O3S |
| Cas No. | 903564-48-7 |
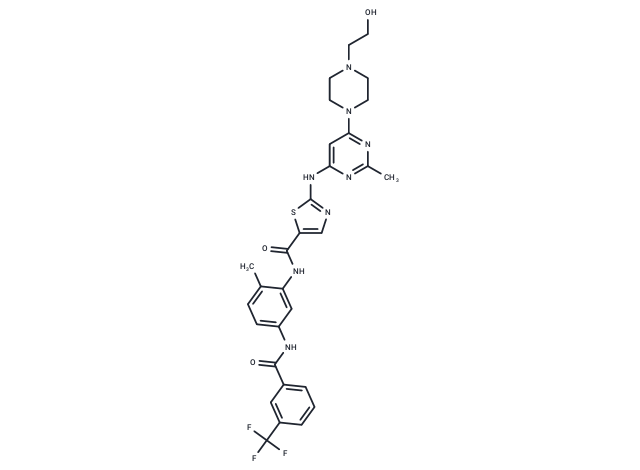
| Smiles | Cc1nc(Nc2ncc(s2)C(=O)Nc2cc(NC(=O)c3cccc(c3)C(F)(F)F)ccc2C)cc(n1)N1CCN(CCO)CC1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.433 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 6.41 mg/mL (10 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.