Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Carbamazepine (NSC-169864) is a tricyclic compound chemically related to tricyclic antidepressants (TCA) with anticonvulsant and analgesic properties. Carbamazepine exerts its anticonvulsant activity by reducing polysynaptic responses and blocking post-tetanic potentiation. Its analgesic activity is not understood; however, carbamazepine is commonly used to treat pain associated with trigeminal neuralgia.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $37 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $42 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $50 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $42 | In Stock |
| Description | Carbamazepine (NSC-169864) is a tricyclic compound chemically related to tricyclic antidepressants (TCA) with anticonvulsant and analgesic properties. Carbamazepine exerts its anticonvulsant activity by reducing polysynaptic responses and blocking post-tetanic potentiation. Its analgesic activity is not understood; however, carbamazepine is commonly used to treat pain associated with trigeminal neuralgia. |
| Targets&IC50 | Na+ channel:131 μM |
| In vitro | In the presence of batrachotoxin, carbamazepine did not alter the binding of scorpion toxin (125I-labeled) to synaptosomes; however, upon the addition of 1.25 μM batrachotoxin, carbamazepine concentration dependently inhibited the enhancement of batrachotoxin-dependent scorpion toxin binding (IC50: 260 μM) via regulatory sites of the toxin alkaloid. Importantly, carbamazepine had no effect on [3H]saxitoxin binding. When acting on rat brain synaptosomes, carbamazepine impeded the binding of [3H]Batrachotoxinin A 20-α-benzoate to the voltage-sensitive sodium channel site (IC50: 131 μM), thereby reducing the ion flow activity of the sodium channels. As the dissociation rate of the ligand from the receptor-ligand complex increased, carbamazepine, despite decreasing receptor affinity, did not change the maximal binding capacity in Scatchard analyses of [3H]Batrachotoxinin A 20-α-benzoate to synaptosomes, suggesting that binding of [3H]Batrachotoxinin A 20-α-benzoate inhibits conformational changes associated with anticonvulsant effects. |
| In vivo | Treatment with Carbamazepine (25 mg/kg) significantly increases the levels of hippocampal dopamine, dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA), striatal homovanillic acid, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, with these effects being dose-dependent. However, a higher dose of Carbamazepine (50 mg/kg) markedly reduces the overall hippocampal homovanillic acid and striatal DOPA and dopamine levels, while not affecting hippocampal dopamine, DOPA, and DOPAC levels, nor overall striatal DOPAC and homovanillic acid. At a dose of Carbamazepine (100 mg/kg, i.p.), there is a dose-dependent significant increase in the concentrations of neuroactive steroids in rat plasma corticosterone. |
| Alias | NSC 169864 |
| Molecular Weight | 236.27 |
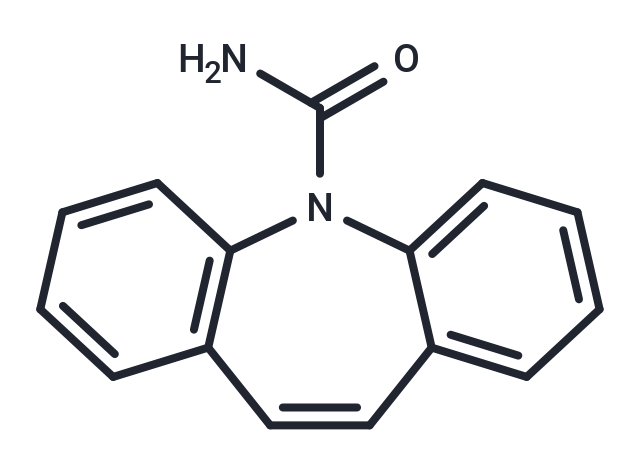
| Formula | C15H12N2O |
| Cas No. | 298-46-4 |
| Smiles | NC(=O)N1C2=CC=CC=C2C=CC2=C1C=CC=C2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.266g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 55 mg/mL (232.78 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 15 mg/mL (63.49 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.