Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Lonidamine (Diclondazolic Acid) is an indazole carboxylic acid derivative, principally inhibiting aerobic glycolytic activity, by its effect on mitochondrially-bound hexokinase (HK).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $33 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $45 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $58 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $75 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $117 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $152 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $373 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $555 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Lonidamine (Diclondazolic Acid) is an indazole carboxylic acid derivative, principally inhibiting aerobic glycolytic activity, by its effect on mitochondrially-bound hexokinase (HK). |
| Targets&IC50 | Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier:2.5 μM (Ki) |
| In vitro | In mice carrying glioma tumors, Lonidamine (160 mg/kg) effectively reduced tumor growth. |
| In vivo | In both normal and tumor cells, Lonidamine reduces oxygen consumption while augmenting aerobic glycolysis in normal cells, thereby inhibiting aerobic glycolysis in tumor cells. The compound induces apoptosis at a concentration of 50 mg/ml in resistant cell lines, including the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 ADR(r) and the LB9 multiform glioblastoma cell line, which exhibit resistance to doxorubicin and nitrosourea. |
| Alias | Diclondazolic Acid, DICA, AF1890 |
| Molecular Weight | 321.16 |
| Formula | C15H10Cl2N2O2 |
| Cas No. | 50264-69-2 |
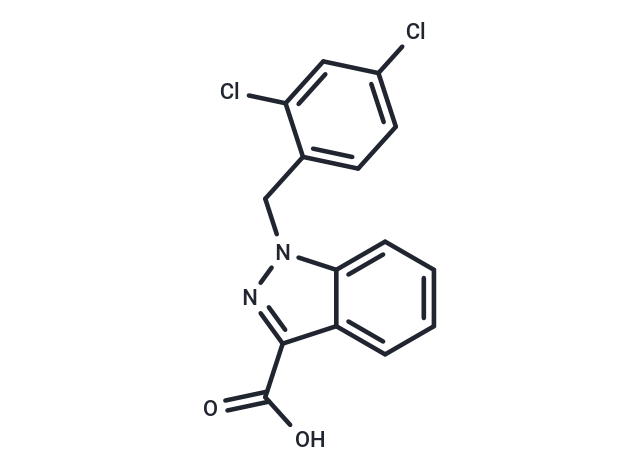
| Smiles | OC(=O)c1nn(Cc2ccc(Cl)cc2Cl)c2ccccc12 |
| Relative Density. | 1.47 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 60 mg/mL (186.82 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 1.6 mg/mL (4.98 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.