Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

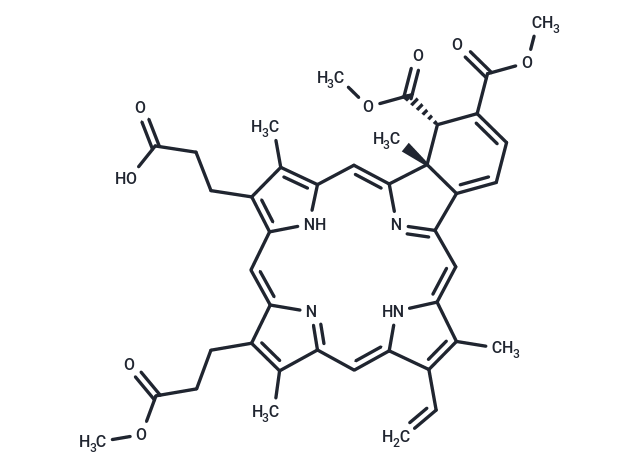
Verteporfin (BPD-MA) is a YAP inhibitor that inhibits YAP-TEAD interactions. Verteporfin is also a photosensitizer used in photodynamic therapy. Verteporfin also induces apoptosis and inhibits autophagy.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $34 | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $77 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $117 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $237 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $385 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $486 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $123 | In Stock |
| Description | Verteporfin (BPD-MA) is a YAP inhibitor that inhibits YAP-TEAD interactions. Verteporfin is also a photosensitizer used in photodynamic therapy. Verteporfin also induces apoptosis and inhibits autophagy. |
| In vitro | Verteporfin metabolizes into a less active form within the body and is rapidly cleared, primarily excreted via feces and to a lesser extent through urine. Its therapy is effective and selectively prevents fluorescein dye leakage from choroidal neovascularization (CNV) induced in experimental monkeys. Verteporfin quickly accumulates in the choroidal vasculature, retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and photoreceptors of established rabbit eyes. Upon intravenous injection in mice, peak tissue levels of Verteporfin are reached within 3 hours, followed by a rapid decline within 24 hours. |
| In vivo | Verteporfin forms a complex with LDL, which may be taken up by proliferating cells (e.g., neovascular endothelial cells) through LDL receptors or endocytosis. The therapy with Verteporfin achieves complete vascular occlusion through thrombosis in the vascular channels following selective endothelial damage. As shown by optical and electron microscopy, Verteporfin therapy selectively induces occlusion in regenerating and detached choroidal capillaries, without altering the overlying photoreceptors or ganglion cells. Verteporfin rapidly exhibits apoptotic changes in conjunction with light, as demonstrated by the activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9 and the cleavage of PARP in HL-60 cells, changes that are inhibited by the broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor ZVAD.fmk. |
| Kinase Assay | Cells (5 × 103) are plated in 96 well plates. Cells are treated the next day for 24 to 48 hours and then assessed for caspase-3 activity by Caspase-Glo-3/7 Assay, as per manufacturer's instructions and a luminescence plate reader. |
| Cell Research | Verteporfin is dissolved in DMSO. PDX cells co-cultured with S17 cells are treated with 16 combinations of verteporfin (60 nM, 120 nM, 180 nM, and 240 nM) and dasatinib (12 nM, 24 nM, 36 nM, and 48 nM). The viabilities of cells treated with each combination are measured after 48 h using FACS Aria flow cytometer. In order to estimate drug interaction between verteporfin and dasatinib, a normalized isobologram and fraction affectedcombination index (CI) plot are made using CompuSyn software. CI values greater than 1.0 indicated antagonistic effects, equal to 1.0 additive effects, and below 1.0 synergistic effects. |
| Alias | CL 318952, BPD-MA |
| Molecular Weight | 718.79 |
| Formula | C41H42N4O8 |
| Cas No. | 129497-78-5 |
| Smiles | COC(=O)CCc1c(C)c2cc3[nH]c(cc4nc(cc5[nH]c(cc1n2)c(CCC(O)=O)c5C)[C@]1(C)[C@H](C(=O)OC)C(=CC=C41)C(=O)OC)c(C)c3C=C |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight,keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 100 mg/mL (139.12 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.