Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Etidronic acid (HEDP) is a diphosphonate which affects calcium metabolism. It inhibits ectopic calcification and slows down bone resorption and bone turnover.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $31 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $35 | In Stock |
| Description | Etidronic acid (HEDP) is a diphosphonate which affects calcium metabolism. It inhibits ectopic calcification and slows down bone resorption and bone turnover. |
| In vitro | Etidronate inhibits directly osteoclastic bone-resorbing activity by pit assay. Etidronate also directly induces apoptosis and disrupts actin rings in osteoclasts. [1] |
| In vivo | Etidronate, when administered s.c. repeatedly at 10 or 40 mg/kg/day, gradually suppresses the adjuvant-induced allodynia In the rats with adjuvant arthritis, as assessed by 10-g von Frey hair. Etidronate (10-40 mg/kg/day) suppresses the adjuvant-induced mechanical allodynia in rat hindpaw. Etidronate (5–10 mg/kg/day) dose-dependently prevents the decrease in bone mineral density (BMD) in the proximal tibia of the arthritic rats. [2] Etidronate inhibits the histidine decarboxylase induction, but not the other inflammatory reactions induced by alendronate. Etidronate (unlike clodronate) also inhibits alendronate-induced BP-line formation in mice (even at 40 mmol/kg). Etidronate (160 mmol/kg) also inhibits the physicochemical changes in the tibia induced by six, weekly injections of alendronate. [3] Etidronate (10 mg/kg) combined with Calcitriol after subtotal nephrectomy (SNx) significantly inhibits thoracic and abdominal aortic calcification 3 weeks after the operation in rats. [4] Etidronate (5 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg) significantly reduces the thoracic and abdominal aortic calcification induced by calcitriol in the renal failure rat. Etidronate (5 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg) also reduces the dysfunction in aortic contraction. Etidronate (5 mg/kg) reverses the reduction in the aortic expression of matrix Gla protein mRNA observed in nephrectomized rats. [5] |
| Alias | HEDPA, HEDP, Etidronate |
| Molecular Weight | 206.03 |
| Formula | C2H8O7P2 |
| Cas No. | 2809-21-4 |
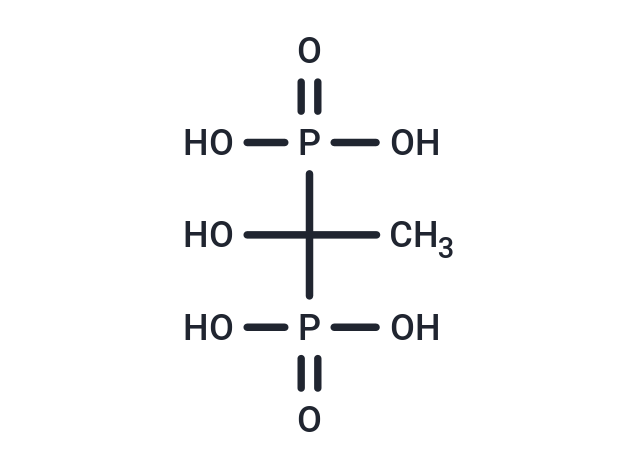
| Smiles | C(P(=O)(O)O)(P(=O)(O)O)(C)O |
| Relative Density. | 1 450 - 1 490 kg/m3. Temperature:20. |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 45 mg/mL (218.41 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.