Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

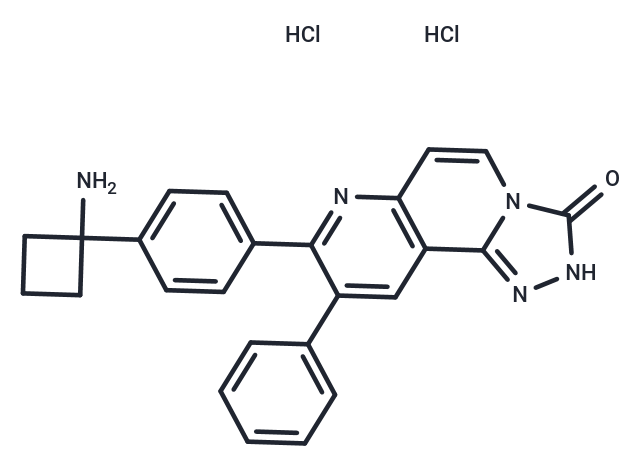
MK-2206 dihydrochloride (MK-2206 2HCl) is a variant Akt inhibitor that inhibits Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3 (IC50=8/12/65 nM) with orally active, highly potent and selective potency. MK-2206 dihydrochloride exhibits antitumor activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | 28 € | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | 44 € | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | 60 € | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | 92 € | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | 139 € | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | 216 € | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | 353 € | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | 582 € | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | 48 € | In Stock |
| Description | MK-2206 dihydrochloride (MK-2206 2HCl) is a variant Akt inhibitor that inhibits Akt1, Akt2, and Akt3 (IC50=8/12/65 nM) with orally active, highly potent and selective potency. MK-2206 dihydrochloride exhibits antitumor activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | Akt3:65 nM (cell free), Akt2:12 nM (cell free), Akt1:8 nM (cell free) |
| In vitro | METHODS: Fourteen tumor cells were treated with MK-2206 dihydrochloride for 72 h. Cell viability was measured by CellTiter-Glo assay. RESULTS: MK-2206 dihydrochloride inhibited the growth of tumor cells with IC50 ranging from 0.1 to 28.6 μmol/L. [1] METHODS: Human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines CNE-2 and HONE-1 were treated with MK-2206 dihydrochloride (0.625-10 μM) for 24-48 h, and the cell cycle was detected by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: MK-2206 dihydrochloride caused a dose-dependent increase in the percentage of cells in G0/G1 phase and a decrease in the number of cells in S phase.MK-2206 dihydrochloride induced cell cycle arrest in G1 phase. MK-2206 dihydrochloride induces cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To detect anti-tumor activity in vivo, MK-2206 dihydrochloride (120 mg/kg three times per week or 360 mg/kg once per week, 30% Captisol) and erlotinib (50 mg/kg five times per week, 0.5% methylcellulose + 0.1% Tween 80) were orally administered to CD1 mice bearing human lung cancer tumor NCI-H292 for two weeks. RESULTS: Three-times-weekly MK-2206 monotherapy was ineffective, and the once-weekly regimen mediated only moderate antitumor efficacy. Although erlotinib alone mediated significant tumor growth inhibition, combination therapy with MK-2206 significantly enhanced its antitumor efficacy, including tumor regression. [1] METHODS: To assay antitumor activity in vivo, MK-2206 dihydrochloride (120 mg/kg in 30% captisol) was administered by gavage to NSG mice bearing human endometrial cancer tumors twice a week for three weeks. RESULTS: MK-2206 dihydrochloride treatment resulted in significant inhibition of the growth of three different types and grades of PDX tumors. [3] |
| Cell Research | Cells were seeded at a density of 2 to 3 × 103 per well in 96-well plates. Twenty-four hours after plating, varying concentrations of the drug, either as a single agent or in combination, were added to the wells. Cell proliferation was determined by using the CellTiter-Glo assay at 72 or 96 hours after dosing. The nature of the drug interaction was evaluated by using the combination index (CI) according to the method of Chou and Talalay. A commercial software package was obtained from Calcusyn. In combination with docetaxel, we tested three treatment sequences: (a) MK-2206 followed by docetaxel—cells were exposed to MK-2206 for 24 hours, and then after washout of MK-2206, cells were treated with docetaxel for an additional 72 hours; (b) docetaxel followed by MK-2206—cells were exposed to docetaxel for 24 hours, and then after washout of docetaxel, cells were treated with MK-2206 for an additional 72 hours; and (c) concurrent treatment—cells were exposed to both MK-2206 and docetaxel for 72 hours [2]. |
| Animal Research | When the mean tumor size reached 0.13 cm3 for the SK-OV-3 or 0.2 cm3 for the NCI-H292, HCC70, PC-3, and NCI-H460 models, the mice were randomized into control and treatment groups with approximately equivalent ranges of tumor volume between groups (n = 5 animals per group). The following vehicles were used to dose the compounds: 30% Captisol (Cydex) for MK-2206; 0.5% methylcellulose + 0.1% Tween 80 for erlotinib; distilled water for lapatinib; 0.73% ethanol in saline for docetaxel; and saline for carboplatin and gemcitabine. The control group received vehicle only. Tumor volume was measured with calipers twice a week. Animal body weight and physical signs were monitored during the experiments. Tumor volume was calculated, taking length to be the longest diameter across the tumor and width to be the perpendicular diameter, by using the following formula: (length × width)2 × 0.5. Relative tumor volume was assessed by dividing the tumor volume on different observation days with the starting tumor volume. Statistical significance was evaluated by using the two-way repeated ANOVA test followed by Dunnett's test or an unpaired t-test [2]. |
| Alias | MK-2206 2HCl |
| Molecular Weight | 480.39 |
| Formula | C25H23Cl2N5O |
| Cas No. | 1032350-13-2 |
| Smiles | Cl.Cl.NC1(CCC1)c1ccc(cc1)-c1nc2ccn3c(n[nH]c3=O)c2cc1-c1ccccc1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) DMSO: 7.5 mg/mL (15.61 mM) 10% DMSO+90% Saline: 0.75 mg/mL (1.56 mM), In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
10% DMSO+90% Saline/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.