Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506) is an orally active, multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits RET, C-RAF, VEGFR2, c-Kit, VEGFR1, and PDGFRβ, exhibiting both antitumor and anti-angiogenic activity.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mg | $30 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $73 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $97 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $147 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $195 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $326 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $52 | In Stock |
| Description | Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506) is an orally active, multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits RET, C-RAF, VEGFR2, c-Kit, VEGFR1, and PDGFRβ, exhibiting both antitumor and anti-angiogenic activity. |
| Targets&IC50 | VEGFR2:4.2 nM (cell free), RET:1.5 nM (cell free), VEGFR1:13 nM (cell free), Raf-1:2.5 nM (cell free), c-Kit:7 nM (cell free), B-Raf (V600E):19 nM (cell free) |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human hepatocellular carcinoma cells Hep3B, PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2 were treated with Regorafenib (0-10 μM) for 72 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT. RESULTS: Regorafenib concentration-dependently decreased the viability of Hep3B cells with an IC50 of about 5 μM. PLC/PRF/5 cells were similarly sensitized to Hep3B cells. However, HepG2 cells were more sensitive, with an IC50 of approximately 1 μM. [1] METHODS: Tumor cells NIH-3T3/VEGFR2, CHO/TIE2, HAoSMC/PDGFR-β and MCF-7/FGFR were treated with Regorafenib (10-3000 nM) for 1 h. The expression levels of the target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Regorafenib inhibited p-VEGFR2, p-TIE2, p-PDGFR-β and p-FGFR. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To test the antitumor activity in vivo, Regorafenib (3-100 mg/kg) was orally administered to NCr nu/nu mice bearing tumors Colo-205 or MDA-MB-231 once daily for nine days. RESULTS: Regorafenib inhibited tumor growth. In the Colo-205 model, Regorafenib at a dose of 10 mg/kg resulted in a TGI of 75% on day 14. In the MDA-MB-231 model, Regorafenib was highly effective at doses as low as 3 mg/kg, resulting in a significant TGI of 81%. [2] METHODS: To assay antitumor activity in vivo, Regorafenib (3-10 mg/kg) was administered orally to NMRI nu/nu mice harboring tumors HT-29 or MDA-MB-231 once daily for twenty-seven days. RESULTS: Regorafenib dose-dependently inhibited HT-29 and MDA-MB-231 tumor growth. [3] |
| Kinase Assay | In vitro assays using recombinant VEGFR2 (murine aa785–aa1367), VEGFR3 (murine aa818–aa1363), PDGFR-b (aa561–aa1106), RAF-1 (aa305–aa648) and BRAFV600E (aa409–aa765) kinase domains were performed as previously described. Initial in vitro kinase inhibition profiling was performed at a fixed 1 μM compound concentration under Millipore standard conditions [10 μM adenosine-50'- triphosphate (ATP) concentration]. Inhibitory concentration of 50% (IC50) values were determined from selected responding kinases, e.g., VEGFR1 and RET. TIE2 kinase inhibition was measured with a homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence (HTRF) assay using a recombinant fusion protein of glutathione-S-transferase, the intracellular domain of TIE2 and the peptide biotin-Ahx-EPKDDAYPLYSDFG as substrate. |
| Cell Research | Each cell line was seeded at 0.3×10^5 cells/2ml of DMEM containing 10% FBS in 35 mm tissue culture dishes. The cells were incubated for 24 h to allow attachment, and then the medium was replaced by fresh culture medium containing Regorafenib at increasing concentrations (1 μM, 2.5 μM, 5 μM, 7.5 μM and 10 μM). In these experimental conditions, the cells were allowed to grow for 72 or 96 h. Time-course experiments on Hep3B cells were performed with 7.5 μM of Regorafenib at short (15, 60, 180 min.), middle (24, 48, 72 and 96 h) or long times (up to seven days). When the cells were treated for long times the drug was replaced with a fresh one. Each experiment included a control with the equivalent concentration of DMSO (solvent control) as the one used for adding Regorafenib. Each experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated 3 times. Subsequent analyses were performed at specific Regorafenib concentrations and incubation times [2]. |
| Animal Research | Female athymic NCr nu/nu mice, kept in accordance with Federal guidelines, were subcutaneously inoculated with 5×10^6 Colo-205 or MDAMB-231 cells or implanted with 1 mm^3 786-O tumor fragments. When tumors reached a volume of ~100 mm^3, regorafenib or vehicle control was administered orally qd×21 in the 786-O model, and qd×9 in the Colo-205 and MDA-MB231 models, respectively, at doses of 100, 30, 10, and 3 mg/kg. Paclitaxel was administered intravenously at 10 mg/kg in ethanol/Cremophor ELV/saline (12.5%/12.5%/75%) every 2 days×5. Tumor size (volume) was estimated twice weekly (l×w^2)/2, and the percentage of tumor growth inhibition (TGI) was obtained from terminal tumor weights (1-T/C100). Mice were weighed every other day starting from the first day of treatment. The general health status of the mice was monitored daily [1]. |
| Alias | Fluoro-Sorafenib, BAY 73-4506 |
| Molecular Weight | 482.82 |
| Formula | C21H15ClF4N4O3 |
| Cas No. | 755037-03-7 |
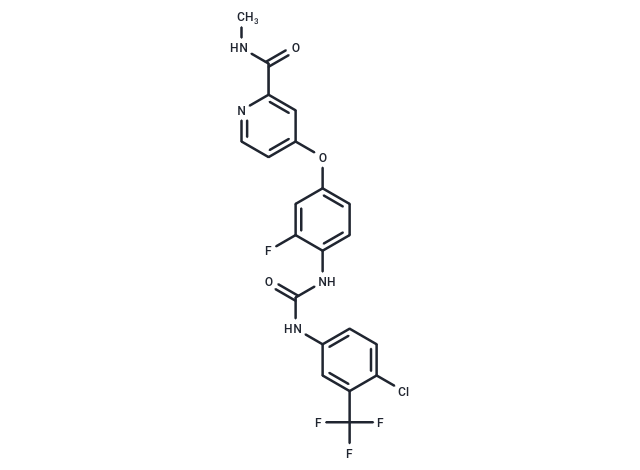
| Smiles | CNC(=O)c1cc(Oc2ccc(NC(=O)Nc3ccc(Cl)c(c3)C(F)(F)F)c(F)c2)ccn1 |
| Relative Density. | 1.491 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 60 mg/mL (124.27 mM), Sonication is recommended. 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 9 mg/mL (18.64 mM), suspension.In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.