Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

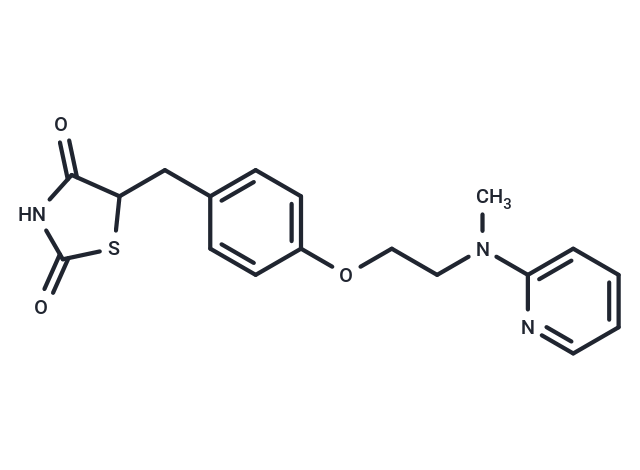
Rosiglitazone (BRL49653) is a PPARγ agonist, TRPC5 activator, and TRPM3 inhibitor with oral activity. Rosiglitazone is also a hypoglycemic agent and a thiazolidinedione insulin sensitizer.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mg | $33 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $82 | In Stock | |
| 200 mg | $147 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $246 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $52 | In Stock |
| Description | Rosiglitazone (BRL49653) is a PPARγ agonist, TRPC5 activator, and TRPM3 inhibitor with oral activity. Rosiglitazone is also a hypoglycemic agent and a thiazolidinedione insulin sensitizer. |
| Targets&IC50 | PPARγ2:100 nM(EC50), PPARγ:60 nM(EC50), PPARγ1:30 nM(EC50) |
| In vitro | Rosiglitazone reduces bone formation rate and increases adipose content within the bone marrow. It decreases the expression of osteoblast-specific genes Runx2/Cbfa1, DLX5, and α1(I) collagen, while expression of the adipocyte-specific fatty acid binding protein AP2 is increased. This drug leads to significant bone loss, evidenced by reductions in bone mass, trabecular width, and number, along with an increase in trabecular separation. Furthermore, in ob/ob mice, rosiglitazone enhances transcription of genes encoding mitochondrial proteins in white adipocytes, which is accompanied by changes in mitochondrial number and structure. |
| In vivo | In certain cell lines, Rosiglitazone reduces cholesterol synthesis independent of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ). The compound significantly enhances the phosphorylation of threonine 172 in the α subunit of AMP-dependent protein kinase, increasing the AMP: ATP ratio. Additionally, Rosiglitazone boosts secretion of adiponectin by up to 2.3-fold from omental cells, while secretion from subcutaneous fat cells remains unaffected. In 3T3-L1 adipocytes, Rosiglitazone alters mitochondrial morphological characteristics and protein profile. It activates complexes containing α1- and α2-AMPK, leading to a marked increase in phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Rosiglitazone also acts as a dominant inhibitor of osteoblastogenesis from mouse marrow in vitro through the activation of PPAR-gamma2. |
| Cell Research | Rosiglitazone is dissolved in DMSO and stored, and then diluted with appropriate medium before use[2]. Human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells are maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 μg/mL Streptomycin and 100 U/mL Penicillin G. SH-SY5Y cells are transfected with the longest isoform of human tau (2N4R) tagged with GFP using lipofectamine. 24 hr after transfection, cells are treated with Rosiglitazone (10 μM, 50 μM) for 24 hr[2]. |
| Alias | BRL49653 |
| Molecular Weight | 357.43 |
| Formula | C18H19N3O3S |
| Cas No. | 122320-73-4 |
| Smiles | C(C1SC(=O)NC1=O)C2=CC=C(OCCN(C)C3=CC=CC=N3)C=C2 |
| Relative Density. | 1.315 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 3.57 mg/mL (9.99 mM), suspension.In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. DMSO: 45 mg/mL (125.9 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.