Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Staurosporine (AM-2282) is a protein kinase inhibitor with ATP-competitive and non-selective inhibitory activity (IC50=6/15/2/3/3000 nM) against PKC, PKA, c-Fgr, phosphorylase kinase and TAOK2. Staurosporine also induces apoptosis.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $56 | In Stock | |
| 2 mg | $79 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $98 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $148 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $259 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $423 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $628 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,350 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $111 | In Stock |
| Description | Staurosporine (AM-2282) is a protein kinase inhibitor with ATP-competitive and non-selective inhibitory activity (IC50=6/15/2/3/3000 nM) against PKC, PKA, c-Fgr, phosphorylase kinase and TAOK2. Staurosporine also induces apoptosis. |
| Targets&IC50 | PKCα:2 nM, PKCη:4 nM, PKCδ:20 nM, PKCγ:5 nM, PKCζ:1086 nM, PKCε:73 nM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human cervical cancer cells HeLa were treated with Staurosporine (1-10 nM) for 72 h, and cell viability was measured by MTT. RESULTS: Staurosporine inhibited the proliferation of Hela cells in a dose-dependent manner, with an IC50 of about 10 nM. [1] METHODS: Human pancreatic cancer cells PaTu 8988t and Panc-1 were treated with Staurosporine (1 μM) for 3-24 h, and cell death was detected by Flow Cytometry. RESULTS: For PaTu 8988t cells, incubation with Staurosporine for 3-24 h significantly increased apoptosis and significantly decreased the number of viable cells; necrosis increased after 6-16 h. For Panc-1 cells, Staurosporine treatment significantly increased apoptosis and significantly decreased the number of viable cells after 9-24 h. The RESULTS were summarized as follows. [2] METHODS: Human hepatocellular carcinoma cells HepG2 were treated with Staurosporine (20 nmol/L) for 6-24 h. The expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Staurosporine significantly inhibited the phosphorylation of mTOR and increased the expression of LC3-II, an autophagy marker protein, suggesting that Staurosporine activates autophagy effectively by inhibiting mTOR. [3] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To assay anti-tumor activity in vivo, Staurosporine (3 mg/kg) and Lapatinib (50 mg/kg) were administered by gavage twice a week for two weeks to Nu/J-Foxn1 Nu/Nu mice harboring human mammary carcinoma tumors JIMT-1. RESULTS: The combination of Staurosporine and Lapatinib inhibited tumor growth in a statistically significant manner. [4] METHODS: To examine the effects on islet β-cell function, Staurosporine (0.4 mg/kg in 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose) was administered intraperitoneally to iPLA2β-/- C57BL6 mice once daily for two weeks. for two weeks. RESULTS: Staurosporine impairs glucose tolerance and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic islets. [5] |
| Kinase Assay | Enzyme assay and binding assay: Protein kinase C is assayed in a reaction mixture (0.25 mL) containing 5 μmol of Tris/HCl, pH 7.5, 2.5 μmol of magnesium acetate, 50 μg of histone II S, 20 μg of phosphatidylserine, 0.88 μg of diolein, 125 nmol of CaCl2, 1.25 nmol of [γ-32]ATP (5-10 × 104 cpm/nmol) and 5 μg of partially purified enzyme. The binding of [3H]PDBu to protein kinase C is determined: Reaction mixture (200 μL contained 4 μmo1 of Tris/malate, pH 6.8, 20 μmol of KCl, 30 nmol of CaC12, 20 μg of phosphatidylserine, 5 μg of partially purified protein kinase C, 0.5% (final concentration) of DMSO,10 pmol of [3H]PDBu (l-3 × 104 cpm/pmol) and 10 μL of various amounts of Staurosporine. |
| Cell Research | Cells are exposed to Staurosporine for ~32 hours. Cells are fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with the DNA-binding dye Hoechst 33342. Cells are visualized under epifluorescence illumination, and the percentage of apoptotic cells (cells with condensed and fragmented DNA) is determined. (Only for Reference) |
| Alias | CGP 41251, Antibiotic AM-2282, AM-2282 |
| Molecular Weight | 466.53 |
| Formula | C28H26N4O3 |
| Cas No. | 62996-74-1 |
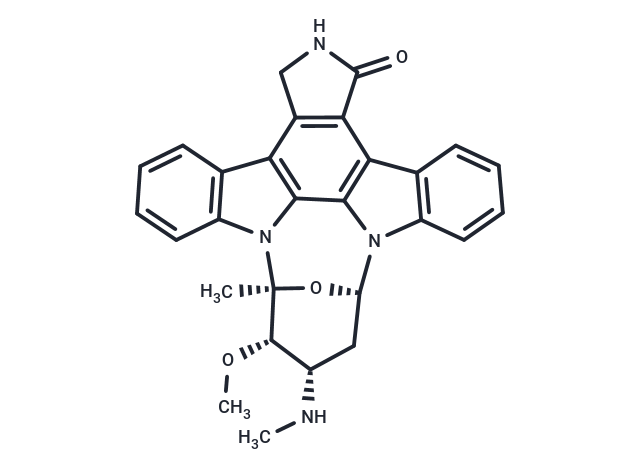
| Smiles | CN[C@H]1C[C@@H]2O[C@@](C)([C@H]1OC)n1c3ccccc3c3c4CNC(=O)c4c4c5ccccc5n2c4c13 |
| Relative Density. | 1.56 g/cm3 (Predicted) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) DMSO: 13.75 mg/mL (29.47 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In Vivo Formulation | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 3.1 mg/mL (6.64 mM), Solution. Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. The formulation provided above is for reference purposes only. In vivo formulations may vary and should be modified based on specific experimental conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.