Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

TTNPB (Ro 13-7410,AGN-191183), a potent RAR agonist, inhibits binding of [3H]tRA of human RARα (IC50: 5.1 nM), β (IC50: 4.5 nM), and γ (IC50: 9.3 nM), respectively.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 mg | $33 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $52 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $79 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $165 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $323 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $488 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $1,060 | In Stock |
| Description | TTNPB (Ro 13-7410,AGN-191183), a potent RAR agonist, inhibits binding of [3H]tRA of human RARα (IC50: 5.1 nM), β (IC50: 4.5 nM), and γ (IC50: 9.3 nM), respectively. |
| Targets&IC50 | RARβ:4.5 nM, RARγ:9.3 nM, RARα:5.1 nM |
| In vitro | By inducing apoptosis, TTNPB (0.25 mg/kg) can inhibit the growth of the MXT-HI and MXT-HS models. |
| In vivo | After 72-hour cultivation in a conditioned medium, TTNPB increases the transcriptional activities of mouse mRARα (EC50: 2.0 nM), β (EC50: 1.1 nM), and γ (EC50: 0.8 nM) in JEG-3 cells. TTNPB exhibits high binding affinity to retinoic acid receptors, thereby inhibiting the binding of [3H]tRA to mRARα (IC50: 3.8 nM), β (IC50: 4.0 nM), and γ (IC50: 4.5 nM). TTNPB inhibits the growth of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells and normal human mammary epithelial cells by inducing a G1 cell cycle arrest. Additionally, TTNPB concentration-dependently reduces the differentiation of ES-D3 cells. |
| Kinase Assay | Binding assays: Binding assays are performed as previously described (Allenby et al., 1993, 1994). Briefly, labeled and unlabeled retinoids are added to nucleosol or cytosolic fractions in ethanol so that the total amount of ethanol added is constant in all tubes and did not exceed 2% of the incubation volume. The receptor preparations are incubated with retinoids at 4°C for 4–6 hr. Sephadex PD-10 desalting columns are used to separate bound radioligand from free radioligand after equilib- rium is achieved. For competitive binding assays, varying concentrations of unlabeled competing ligand are incubated with the appropriate nucleosol or cytosol in the presence of a fixed concentration of [3H]tRA (sp. act. 49.3 Ci/mmol) or [3H]9-cis RA (sp. act. 24.0 Ci/mmol). Final concentrations of [3H] tRA and [3H]9-cis RA for nuclear receptor binding assays are 5 nM. Final concentrations of [3H] tRA for CRABP binding assays is 30 nM. The IC50s are calculated as described above (DeLean et al., 1978). For saturation kinetics, increasing concentrations of radiolabeled ligand ([3H]tRA sp. act. 49.3 Ci/mmol, [3H]TTNPB sp. act. 5.5 Ci/ mmol) are added to the nucleosol of the appropriate receptor subtype in the presence (nonspecific binding) or absence (total binding) of a 100-fold molar excess of the corresponding unlabeled retinoid. Specific binding is defined as the total binding minus nonspecific binding. Saturation kinetics are calculated as previously described (Scatchard, 1949; Grippo and Gudas, 1987; Levin et al., 1992). |
| Cell Research | Human mammary epithelial cells are maintained in Mammary Epithelial Basal Medium (MEBM) supplemented with the Mammary Epithelial Growth Media (MEGM) bullet kit. 184 and 184B5 cells are maintained in MEBM sodium-bicarbonate free (MEBM-SBF) supplemented with the MEGM bullet kit, isoproterenol (10 μM), and transferrin (5 μg/ml). MCF10A cell lines are maintained in DME/F12 containing 5% heat inactivated horse serum, penicillin/streptomycin (100 μg/ml and 100 μg/ml), hydrocortisone (1.4 μM), insulin (10 μg/ml), choleratoxin (100 ng/ml), and EGF (20 ng/ml). Breast cancer cell lines are maintained in Improved MEM Zinc Option containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% glutamine, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. For growth assays, cells are treated with the different retinoids for the specified number of days with media and treatment changes every other day in T47D cells and every 2 days in 184 cells. Cell proliferation is measured according to the protocol for the CellTiter 96 Aqueous Non-Radioactive Cell Proliferation Assay. This colorimetric assay determines the number of viable cells in a sample. Each point represents samples done in quadruplicate.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | Ro 13-7410,AGN-191183, Ro 13-7410, Arotinoid acid, AGN191183 |
| Molecular Weight | 348.48 |
| Formula | C24H28O2 |
| Cas No. | 71441-28-6 |
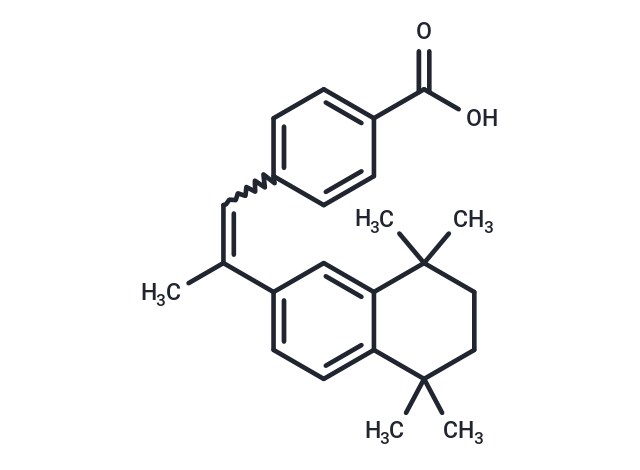
| Smiles | CC(=Cc1ccc(cc1)C(O)=O)c1ccc2c(c1)C(C)(C)CCC2(C)C |
| Relative Density. | 1.06 g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Solubility Information | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 0.18 mg/mL (0.52 mM), In vivo: Please add co-solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. DMSO: < 1 mg/ml |

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.