Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Erlotinib (NSC-718781) is an EGFR inhibitor (IC50: 2 nM). It is used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg | $40 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $48 | In Stock | |
| 500 mg | $72 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Erlotinib (NSC-718781) is an EGFR inhibitor (IC50: 2 nM). It is used for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. |
| Targets&IC50 | EGFR:2 nM (cell free) |
| In vitro | Erlotinib is a direct-acting inhibitor of human EGFR tyrosine kinase with an IC50 of 2 nM and reduces EGFR autophosphorylation in intact tumor cells with an IC50 of 20 nM. Erlotinib is also a potent inhibitor of the recombinant intracellular (kinase) domain of the EGFR (IC50: 1 nM). The proliferation of DiFi cells is strongly inhibited by Erlotinib with an IC50 of 100 nM for an 8-day proliferation assay[1]. |
| In vivo | Erlotinib (20 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly attenuates Cisplatin (CP)-induced body weight (BW) loss when compared to the CP+vehicle (V) rats (P<0.05). Erlotinib treatment significantly improves renal function in CP-N(normal control group, NC) rats. The CP+Erlotinib (E) rats show significant reduction of the levels of Serum creatinine (s-Cr) (P<0.05), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (P<0.05), urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) index (P<0.05), and significant increase of urine volume (UV) (P<0.05) and Cr clearance (Ccr) (P<0.05) compare to the CP+V rats [2]. Erlotinib inhibits tumor growth in human head and neck carcinoma HN5 tumor xenografts in mice with an ED50 value of 9 mg/kg [3]. |
| Kinase Assay | 96-well plates are coated by incubation overnight at 37 °C with 100 μL per well of 0.25 mg/mL PGT in PBS. Excess PGT is removed by aspiration, and the plate is washed 3 times with washing buffer (0.1% Tween 20 in PBS). The kinase reaction is performed in 50 μL of 50 mM HEPES (pH 7.3), containing 125 mM sodium chloride, 24 mM magnesium chloride, 0.1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 20 μM ATP, 1.6 μg/mL EGF, and 15 ng of EGFR, affinity purified from A431 cell membranes. Erlotinib HCl in DMSO is added to give a final DMSO concentration of 2.5%. Phosphorylation is initiated by addition of ATP and proceeded for 8 minutes at room temperature, with constant shaking. The kinase reaction is terminated by aspiration of the reaction mixture and is washed 4 times with washing buffer. Phosphorylated PGT is measured by 25 minutes of incubation with 50 μL per well HRP-conjugated PY54 anti-phosphotyrosine antibody, diluted to 0.2 μg/mL in blocking buffer (3% BSA and 0.05% Tween 20 in PBS). The antibody is removed by aspiration, and the plate is washed 4 times with washing buffer. The colorimetric signal is developed by addition of TMB Microwell Peroxidase Substrate, 50μL per well, and stopped by the addition of 0.09 M sulfuric acid, 50 μL per well. Phosphotyrosine is estimated by measurement of absorbance at 450 nm. The signal for controls is typically 0.6-1.2 absorbance units, with essentially no background in wells without AlP, EGFR, or PGT and is proportional to the time of incubation for 10 minutes [1]. |
| Cell Research | Exponentially growing cells are seeded in 96-well plastic plates and exposed to serial dilutions of erlotinib (30 nM-20 μM), pemetrexed, or the combination at a constant concentration ratio of 4:1 in triplicates for 72 h. Cell viability is assayed by cell count and the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. Growth inhibition is expressed as the percentage of surviving cells in drug-treated versus PBS-treated control cells (which is considered as 100% viability). The IC50 value is the concentration resulting in 50% cell growth inhibition by a 72-h exposure to the drug(s) compared with untreated control cells and is calculated by the CalcuSyn software [4]. |
| Animal Research | Six-week-old male SD rats weighing 180 to 210 g are used. Cisplatin (CP) is freshly prepared in saline at a concentration of 1 mg/mL and then injected intraperitoneally in SD rats (n=28) at a dose of 7 mg/kg on day 0. To investigate the effect of Erlotinib, 28 CP-N rats are divided into two groups. Separate groups (n=14) each of animals are administered with either Erlotinib (20 mg/kg) (CP+E, n=14) or vehicle (CP+V, n=14) daily by oral gavage from the day -1 (24 hours prior to the CP injection) to day 3. Vehicle-treated groups receive an equivalent volume of saline. Five male SD rats at the age of 6 weeks are used as a normal control group (NC, n=5). The NC rats are given an equivalent volume of saline daily by oral gavage from the day -1 to day 3. At day 4 (96 hours after CP injection), each rat is anesthetized and sacrificed by exsanguination after the cardiac puncture; blood is collected by cardiac puncture and kidneys are collected. Renal tissue is divided; separate portions are snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen or fixed in 2% paraformaldehyde/phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for later use. All surgery is performed under diethyl ether gas anesthesia, and all efforts are made to minimize suffering [2]. |
| Alias | R1415, OSI-744, NSC 718781, CP358774 |
| Molecular Weight | 393.44 |
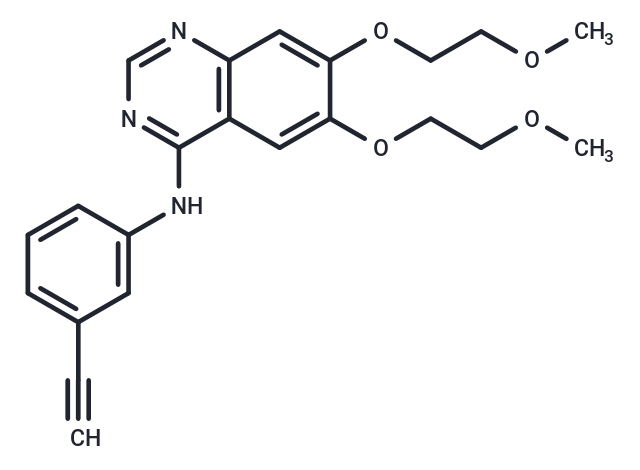
| Formula | C22H23N3O4 |
| Cas No. | 183321-74-6 |
| Smiles | N(C=1C2=C(C=C(OCCOC)C(OCCOC)=C2)N=CN1)C3=CC(C#C)=CC=C3 |
| Relative Density. | 1.24 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline: 7.2 mg/mL (18.3 mM), suspension.In vivo: Please add the solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. DMSO: 60 mg/mL (152.5 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) Ethanol: 12 mg/mL (30.5 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ethanol/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.