Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Primaquine diphosphate is the phosphate salt form of primaquine, a synthetic, 8-aminoquinoline derivative with antimalarial properties. Although its mechanism of action is unclear, primaquine bind to and alter the properties of protozoal DNA. This agent eliminates tissue (exo-erythrocytic) malarial infection, preventing the development of the erythrocytic forms of the parasite which are responsible for relapses in Plasmodium vivax and ovale malaria. Primaquine is active against late hepatic stages (hypnozoites, schizonts).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $66 | In Stock |
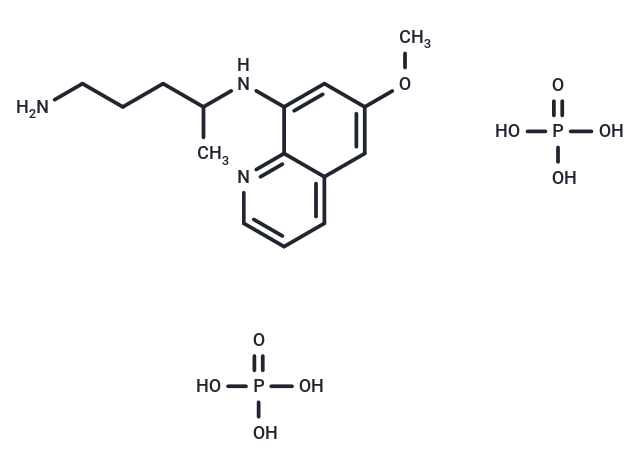
| Description | Primaquine diphosphate is the phosphate salt form of primaquine, a synthetic, 8-aminoquinoline derivative with antimalarial properties. Although its mechanism of action is unclear, primaquine bind to and alter the properties of protozoal DNA. This agent eliminates tissue (exo-erythrocytic) malarial infection, preventing the development of the erythrocytic forms of the parasite which are responsible for relapses in Plasmodium vivax and ovale malaria. Primaquine is active against late hepatic stages (hypnozoites, schizonts). |
| In vivo | Primaquine effectively counters all exoerythrocytic forms of parasites and is used in conjunction with other antimalarial drugs to treat vivax and ovale malaria. It remains an efficacious malaria-blocking agent, exhibiting notable activity against the gametocytes of all human malaria, including multidrug-resistant strains of P. falciparum. The specific mechanism by which Primaquine eliminates P. falciparum and gametocytes is unclear, but studies suggest it involves disruptions to the parasite's mitochondrial metabolism, impairing coenzyme Q's role as an electron carrier in the respiratory chain, and potential generation of highly reactive metabolites leading to increased oxidative potential. Primaquine can block calcium-release-activated channels in rat megakaryocytes and may also act as an inhibitor of vesicular transport. It inhibits protein transport (IC50: 50 μM) and vesicle budding in donor cell membranes. Primaquine significantly suppresses the recycling of phagocytosed proteins to the plasma membrane and inhibits potassium channel currents by blocking muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. It also inhibits human erythrocyte membrane acetylcholinesterase (IC33: 30 μM) and affects the sodium channels in isolated rat ventricular muscle and myocytes. |
| Alias | Primaquine phosphate, Primaquine bisphosphate |
| Molecular Weight | 455.34 |
| Formula | C15H21N3O·2H3PO4 |
| Cas No. | 63-45-6 |
| Smiles | CC(CCCN)Nc1c2c(cc(c1)OC)cccn2.OP(=O)(O)O.OP(=O)(O)O |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 60 mg/mL (131.77 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) H2O: 83 mg/mL (182.28 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.