Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

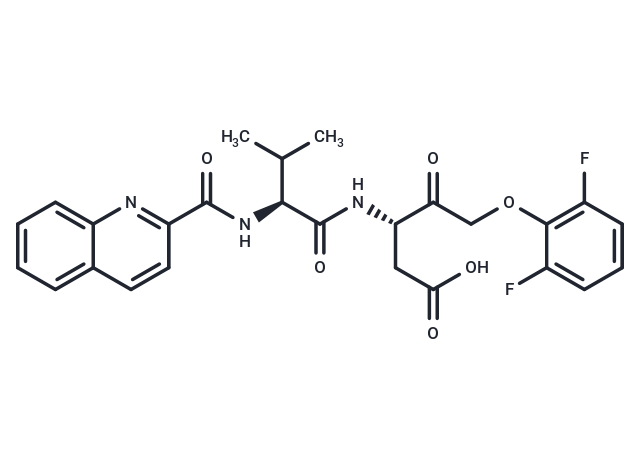
Q-VD-OPH (Quinoline-Val-Asp-Difluorophenoxymethylketone) is a pan-caspase inhibitor with potent antiapoptotic properties.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $47 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $87 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $147 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $237 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $368 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $547 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $98 | In Stock |
| Description | Q-VD-OPH (Quinoline-Val-Asp-Difluorophenoxymethylketone) is a pan-caspase inhibitor with potent antiapoptotic properties. |
| Targets&IC50 | Caspase-8:25 nM-400 nM, Caspase-1:25 nM-400 nM, Caspase-3:25 nM-400 nM, Caspase-9:25 nM-400 nM |
| In vitro | Q-VD-OPh (5-100 μM) potently inhibits Actinomycin D-induced DNA laddering and subsequent apoptosis with minimal toxicity in WEHI 231 cells. Q-VD-OPh prevents caspase mediated cleavage of PARP and activation of the major initiator and effector caspases. [2] Q-VD-OPh protects cardiac myocytes from virus-induced apoptosis in vitro. [4] |
| In vivo | Q-VD-OPh inhibits caspase-1 activity, IL-18 protein expression, and neutrophil infiltration during ischemic ARF in mice. [3] In vivo, caspase inhibition by Q-VD-OPh provides protection from virus-induced myocardial injury, with a significant reduction in caspase-3 activity. [4] In TgCRND8 mice, Q-VD-OPh inhibits caspase-7 activation and limits the pathological changes associated with tau, including caspase cleavage. [5] |
| Kinase Assay | Enzyme assay is conducted in buffer containing 25 mM Tris, pH 8.0, 1 mM DTT, 1 mM spermine, 50 mM KCl, 0.01% Nonidet P-40, and 1 mM MgCl2. PARP reaction contains 0.1 μCi [3H]NAD+ (200?000 DPM), 1.5 μM NAD+, 150 nM biotinylated NAD+, 1 μg/mL activated calf thymus, and 1?5 nM PARP-1. Autoreactions utilizing SPA bead-based detection are carried out in 50 μL volumes in white 96-well plates. Compounds (e.g., MK-4827) are prepared in 11-point serial dilution in 96-well plate, 5 μL/well in 5% DMSO/Water (10× concentrated). Reactions are initiated by adding first 35 μL of PARP-1 enzyme in buffer and incubating for 5 min at room temperature and then 10 μL of NAD+ and DNA substrate mixture. After 3 h at room temperature, these reactions are terminated by the addition of 50 μL of streptavidin-SPA beads (2.5 mg/mL in 200 mM EDTA, pH 8). After 5 min, they are counted using a TopCount microplate scintillation counter. IC50 data is determined from inhibition curves at various substrate concentrations[1]. |
| Cell Research | Caspase inhibitors are added at the indicated concentrations 30 minutes prior to the addition of apoptotic stimuli. Viability and cell number are determined by trypan blue exclusion from three random fields of greater than 200 cells/field. All experiments are performed a minimum of three times.(Only for Reference) |
| Alias | Quinoline-Val-Asp-Difluorophenoxymethylketone |
| Molecular Weight | 513.5 |
| Formula | C26H25F2N3O6 |
| Cas No. | 1135695-98-5 |
| Smiles | CC(C)[C@H](NC(=O)c1ccc2ccccc2n1)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)COc1c(F)cccc1F |
| Relative Density. | 1.346 g/cm3 at 20℃ |
| Storage | keep away from moisture,store at low temperature | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | Ethanol: 100 mg/mL (194.74 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 50 mg/mL (97.37 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/Ethanol
Ethanol
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.