Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

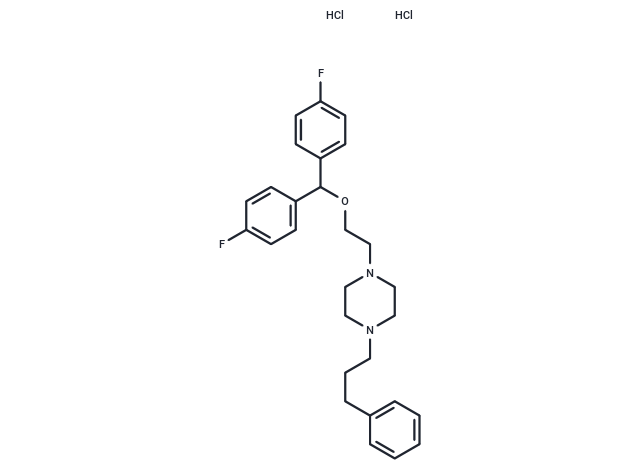
Vanoxerine dihydrochloride (GBR-12909 dihydrochloride) is a potent inhibitor of dopamine uptake (IC50: 1-51 nM).
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg | $44 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $78 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $123 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $179 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $31 | In Stock |
| Description | Vanoxerine dihydrochloride (GBR-12909 dihydrochloride) is a potent inhibitor of dopamine uptake (IC50: 1-51 nM). |
| Targets&IC50 | Dopamine uptake:1-51 nM |
| In vivo | In 9 SP dogs, 11 episodes each of sustained (>10 minutes) AF and AFL were induced. Electrophysiological studies were performed before and after infusion of vanoxerine, which effectively terminated AF and AFL in 19 of 22 episodes. Simultaneous multisite mapping during 3 AF and 3 AFL episodes demonstrated that termination of each arrhythmia occurred with termination of the driver (a reentrant circuit) following an increase in tachycardia CL. Except for conduction in an area of slow conduction in the driver's reentrant circuit, vanoxerine did not significantly affect intraatrial or atrioventricular conduction time, QRS duration, or QT/QTc intervals. Ventricular refractoriness prolonged minimally during ventricular pacing at 400 and 333 ms (176 +/- 16 ms to 182 +/- 16 ms; 173 +/- 11 ms to 178 +/- 18 ms, respectively). Vanoxerine minimally increased (mean 0.7 mA) atrial stimulus threshold for capture[1].Vanoxerine dihydrochloridealso blocks ligand binding to sigma receptors in rat brain (IC50 = 48 nM)[2]. |
| Alias | I893 dihydrochloride, GBR-12909 dihydrochloride |
| Molecular Weight | 523.49 |
| Formula | C28H34Cl2F2N2O |
| Cas No. | 67469-78-7 |
| Smiles | Cl.Cl.Fc1ccc(cc1)C(OCCN1CCN(CCCc2ccccc2)CC1)c1ccc(F)cc1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 9.4 mg/mL (17.96 mM) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.