Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

L-Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) is a natural product that is a potent reducing agent and antioxidant. L-Ascorbic acid functions in fighting bacterial infections, in detoxifying reactions, and in the formation of collagen. L-Ascorbic acid is used in the treatment of scurvy.
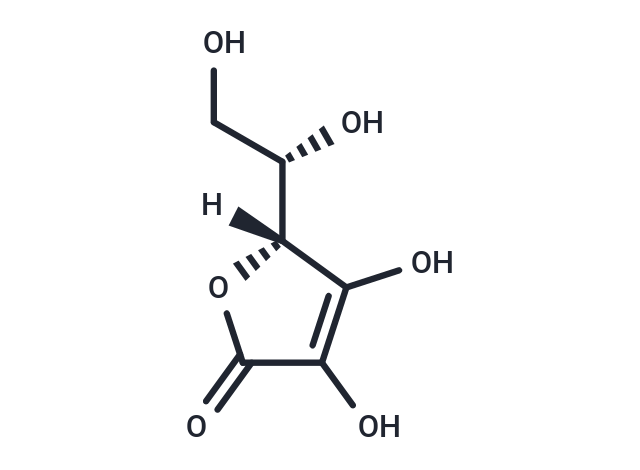
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $42 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $30 | In Stock |
| Description | L-Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) is a natural product that is a potent reducing agent and antioxidant. L-Ascorbic acid functions in fighting bacterial infections, in detoxifying reactions, and in the formation of collagen. L-Ascorbic acid is used in the treatment of scurvy. |
| In vitro | METHODS: Human osteosarcoma cells MG-63 were treated with L-Ascorbic acid (62.5-1000 µM) for 3-24 h. Cell viability was measured by XTT Assay. RESULTS: Cell viability was consistently >95% when cells were treated with L-Ascorbic acid at concentrations of 0-250 µM. When higher concentrations were used, a dose-dependent decrease in cell viability was observed. [1] METHODS: Melanoma cells WM1366 were treated with L-Ascorbic acid (5-50 µM) for 24 h. The expression levels of target proteins were measured using Western Blot. RESULTS: The lowest concentration of L-Ascorbic acid (5 µM) significantly reduced the normoxic expression of HIF-1α protein in human melanoma cell lines. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: L-Ascorbic acid (1-4.5 g/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to irradiated C57BL/6 mice to detect radioprotective activity. RESULTS: Administration of 3 g/kg L-Ascorbic acid immediately after exposure significantly increased the survival rate of mice after 7-8 Gy WBI. However, administration of less than 3 g/kg L-Ascorbic acid was ineffective, and 4 g/kg and above was harmful to mice. [3] METHODS: To investigate the effects on amnesia, L-Ascorbic acid (60-160 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to diazepam, scopolamine, and aging-induced amnesic Swiss mice once daily for 3-8 days. RESULTS: L-Ascorbic acid improved learning and memory in aging mice, as evidenced by decreased transfer latency and increased descending latency. [4] |
| Alias | Vitamin C, L-Ascorbate, L(+)-Ascorbic acid, Ascorbic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 176.12 |
| Formula | C6H8O6 |
| Cas No. | 50-81-7 |
| Smiles | [C@@H](CO)(O)[C@@]1(C(O)=C(O)C(=O)O1)[H] |
| Relative Density. | 1.7 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 35.7 mg/mL (202.7 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 60 mg/mL (340.68 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.