Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

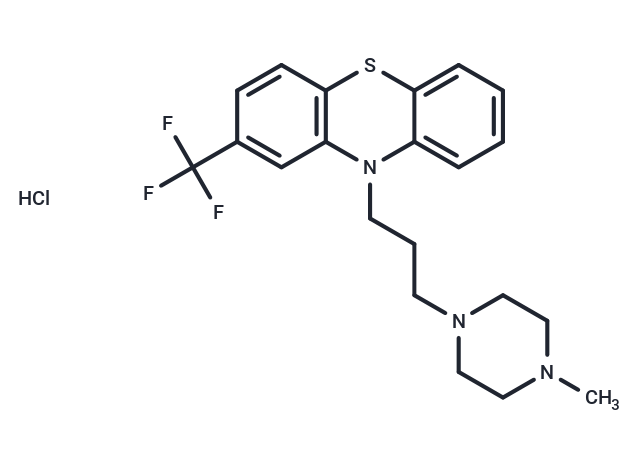
Trifluoperazine dihydrochloride (SKF5019) is a potent dopamine D2 receptor inhibitor used as an antipsychotic and an antiemetic.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 mg | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Trifluoperazine dihydrochloride (SKF5019) is a potent dopamine D2 receptor inhibitor used as an antipsychotic and an antiemetic. |
| Targets&IC50 | D2 receptor:1.1 nM |
| In vitro | Trifluoperazine binds to α1A- and α1B-adrenoceptor with Ki value of 27.6 nM and 19.2 nM, respectively, with α1B/α1A ratio of 0.7. [2] Trifluoperazine inhibits Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) with MICs of 7.6 μg/mL. [3] Trifluoperazine (< 14.78 mM) suppresses the activities of the mouse splenic NK cell cytotoxicity and the effector-target cell conjugation in a dose dependent manner. Trifluoperazine suppresses interferon-alpha or interleukin-2 induced augmentation of the cytolytic activity of NK cells. [4] Trifluoperazine inhibits the gene expression of voltage-dependent potassium channel Kv2.1 from human brain (hKv2.1). [5] |
| In vivo | Trifluoperazine dose dependently decreases avoidance responses and increases response failures in rats where behavior is maintained under a discrete-trial avoidance. [6] |
| Alias | Urinox, Trifluoperazine 2HCl, SKF5019 |
| Molecular Weight | 480.43 |
| Formula | C21H26Cl2F3N3S |
| Cas No. | 440-17-5 |
| Smiles | Cl.CN1CCN(CCCN2C3=CC=CC=C3SC3=C2C=C(C=C3)C(F)(F)F)CC1 |
| Relative Density. | no data available |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | H2O: 88 mg/mL (183.17 mM), Sonication is recommended. DMSO: 82 mg/mL (170.68 mM), Sonication is recommended. Ethanol: 89 mg/mL (185.25 mM), Sonication is recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO/H2O/Ethanol
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.