Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Valproic Acid (2-Propylpentanoic Acid) is an HDAC inhibitor that inhibits HDAC1 activity, induces HDAC2 degradation, and is orally active. Valproic Acid can be used in epilepsy and bipolar disorder research.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 g | $50 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $50 | In Stock |
| Description | Valproic Acid (2-Propylpentanoic Acid) is an HDAC inhibitor that inhibits HDAC1 activity, induces HDAC2 degradation, and is orally active. Valproic Acid can be used in epilepsy and bipolar disorder research. |
| Targets&IC50 | HDAC1:0.4 mM |
| In vitro | METHODS: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell lines TE9, TE10, TE11, and TE14 were treated with Valproic Acid (0.01-5 mM) for 72 h, and cell viability was assayed using MTT Assay. RESULTS: Valproic Acid inhibited the viability of all ESCC cells in a dose-dependent manner. The IC50 values of Valproic Acid ranged from 1.02-2.15 mM in each cell line. [1] METHODS: Mouse teratoma cells, F9, and human cervical cancer cells, HeLa, were treated with Valproic Acid (0.25-5 mM) for 4-24 h. The expression levels of target proteins were detected by Western Blot. RESULTS: Only trace amounts of acetylated histones were detected in untreated F9 or HeLa cells. Treatment with Valproic Acid at concentrations as low as 0.25 mM increased the amount of acetylated histone H4, and significant acetylation was found with 2 mM Valproic Acid. [2] |
| In vivo | METHODS: To study the effects on Machado Joseph disease (MJD), Valproic Acid (200 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally to the CMVMJD135 mouse model five times per week for twenty-five weeks. RESULTS: Chronic Valproic Acid treatment had limited effects on motor deficits in these mice, observed primarily in the late stages of locomotor swimming, beam swimming, rotational bar and spontaneous motor activity tests, and did not alter ATXN3 inclusion body loads and astrocyte proliferation in affected brain regions. [3] METHODS: To assay antitumor activity in vivo, Valproic Acid (500 mg/kg, 10% DMSO 25% w/v Kleptose HPB buffer) was administered by gavage to BALB/c nude mice harboring the human AML tumor, Kasumi-1, once daily for twelve days. RESULTS: Valproic Acid inhibited tumor growth in mice transplanted with Kasumi-1 cells. At the end of the experiment, the incidence of IR in the Valproic Acid group was 57.25%. [4] |
| Alias | VPA, Sodium valproate, Depakine, 2-Propylvaleric Acid, 2-Propylpentanoic Acid |
| Molecular Weight | 144.21 |
| Formula | C8H16O2 |
| Cas No. | 99-66-1 |
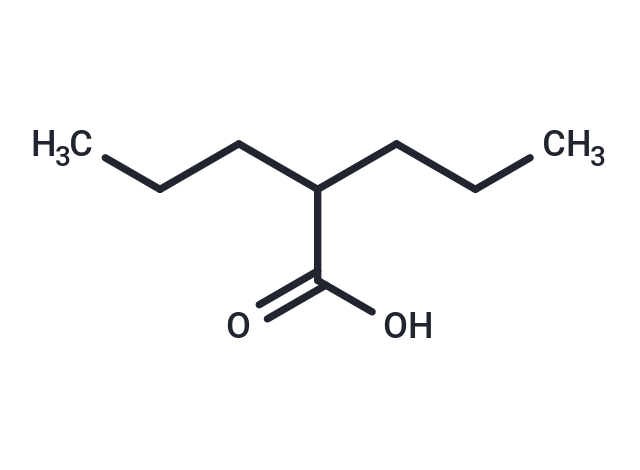
| Smiles | CCCC(CCC)C(O)=O |
| Relative Density. | 0.9g/mLat 25°C(lit.) |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | 5% DMSO+95% Saline: 5 mg/mL (34.67 mM), In vivo: Please add co-solvents sequentially, clarifying the solution as much as possible before adding the next one. Dissolve by heating and/or sonication if necessary. Working solution is recommended to be prepared and used immediately. DMSO: 100 mg/mL (693.43 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 1 mg/mL (6.93 mM), Sonication and heating are recommended. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/5% DMSO+95% Saline/DMSO
5% DMSO+95% Saline/DMSO
DMSO
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.