Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Verapamil hydrochloride (Verapamil HCl) is a calcium channel blocker that is a class IV anti-arrhythmia agent.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 500 mg | $41 | In Stock | |
| 1 g | $48 | In Stock | |
| 1 mL x 10 mM (in DMSO) | $45 | In Stock |
| Description | Verapamil hydrochloride (Verapamil HCl) is a calcium channel blocker that is a class IV anti-arrhythmia agent. |
| In vitro | Verapamil exhibits antiarrhythmic properties, reduces myocardial oxygen consumption in rats, and preserves Cx43 protein. |
| In vivo | Verapamil and Diltiazem essentially inhibit the hydrolase activity of recombinant CES2, with inhibition constants (Ki) of 0.25 ± 0.02 μM and 3.84 ± 0.99 μM, respectively. |
| Cell Research | Verapamil is dissolved in DMSO and stored, and then diluted with appropriate media before use[1]. Cells (1×105) are treated with 10 nM Bortezomib and/or 70 μM Verapamil for 16 hours and incubated for another 4 hours with Alamar-Blue. Activity of the mitochondrial dehydrogenase results in conversion of the coloring, which is followed by measurement of the absorption using a spectrophotometer[1]. |
| Alias | Verapamil HCl, Manidon, Calcan hydrochloride, (±)-Verapamil hydrochlorid |
| Molecular Weight | 491.06 |
| Formula | C27H39ClN2O4 |
| Cas No. | 152-11-4 |
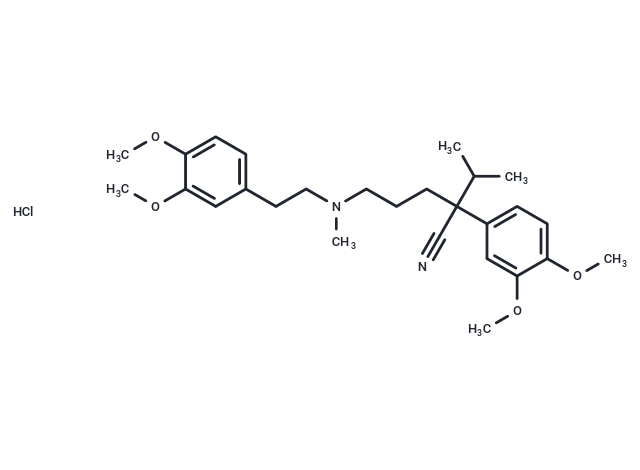
| Smiles | Cl.COc1ccc(CCN(C)CCCC(C#N)(C(C)C)c2ccc(OC)c(OC)c2)cc1OC |
| Relative Density. | 1.058g/cm3 |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 50 mg/mL (101.82 mM), Sonication is recommended. H2O: 24.6 mg/mL (50.1 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
H2O/DMSO
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.