- Remove All

Article | 11 Nov 2023
By TargetMol
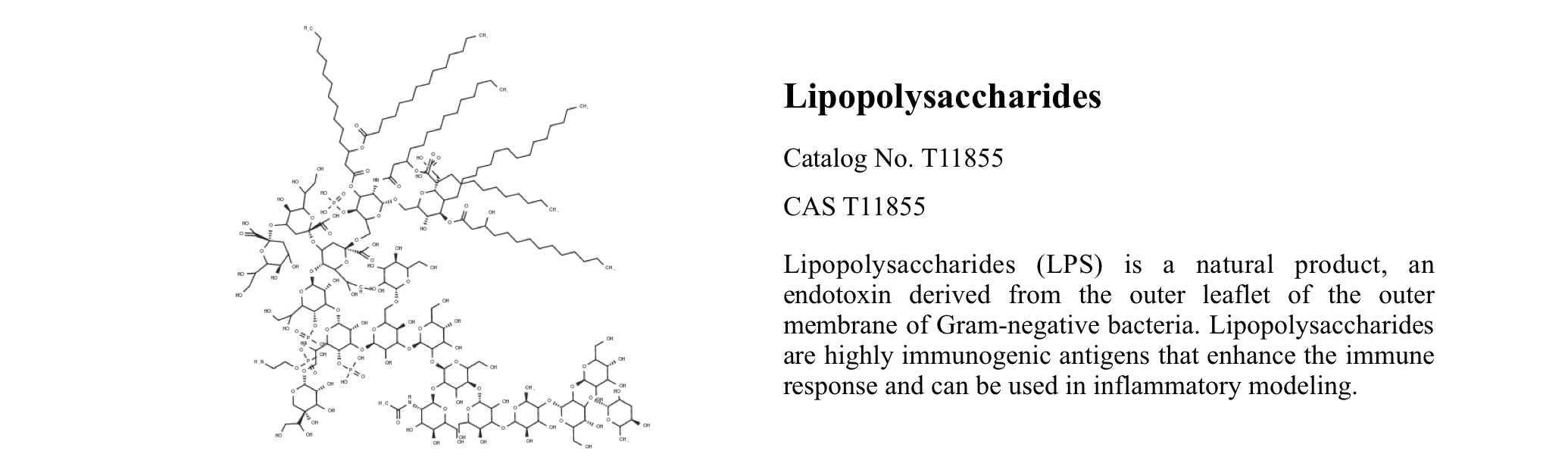
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS), T11855,unique components of the cell membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, are located in the outer membrane and are exposed on the cell surface of non-capsulated bacteria. LPS contributes to maintaining the integrity of the outer membrane and protecting the bacterium from damage by bile salts and lipophilic antibiotics.
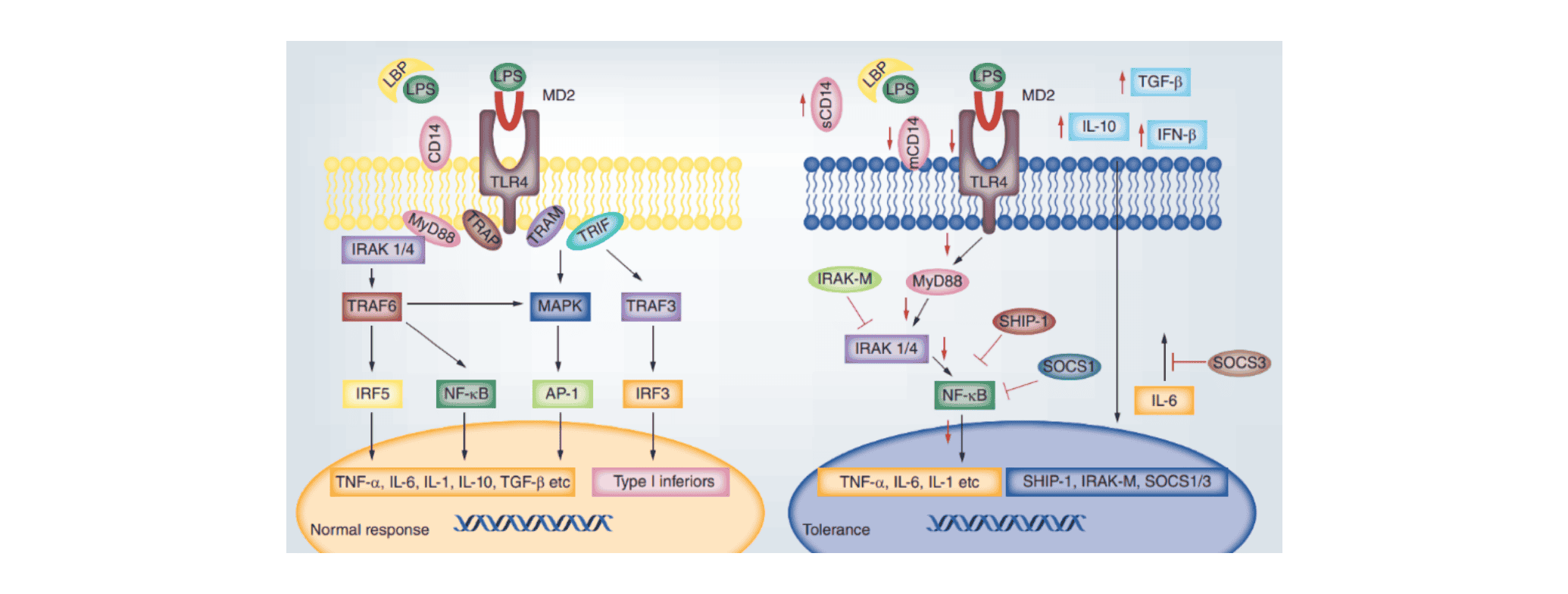
Mechanism of Action
LPS can initiate a cascade of immune stimuli and toxic pathophysiological activities in the body, including the release of endotoxins that can cause septic shock. When bacteria invade the human body, they release their LPS on the cell surface. Initially, LPS binds to lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), which transports LPS to the membrane surface of immune cells, where it interacts with the membrane protein CD14. Subsequently, CD14 transports LPS to Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and myeloid differentiation protein-2 (MD2), forming a protein complex that activates the expression of downstream cytokines and triggers an immune-inflammatory response.
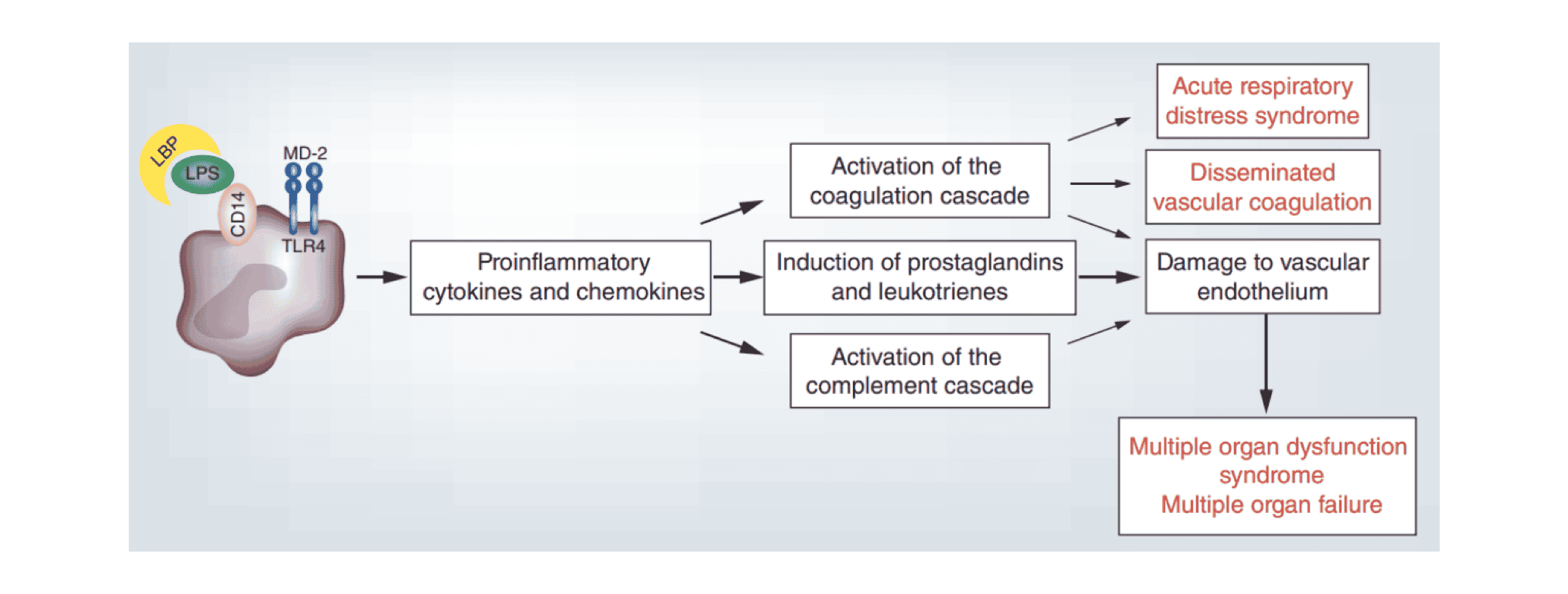
Biological Applications
LPS is one of the most effective activators of the mammalian immune system without toxicological effects. However, as a nonspecific immunogen, when entering the microcirculation, LPS interacts with effector cells, activates the immune cells of the body, (e.g., monocytes, B-lymphocytes, macrophages, etc.) and stimulates the secretion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-2 (IL-2), interleukin-6 (IL-6), thromboxane A2 (TXA2), reactive oxygen species (ROS), nitric oxide (NO), and other biologically active molecules. This can lead to clinical syndromes such as fever, diarrhea, systemic inflammation response, coagulation dysfunction, multiple organ failure, and even shock.
LPS is commonly extracted for the study of its structure, biosynthetic pathways, metabolism, toxicologic pathophysiology, immune responses, and is used in various life science research including the induction of growth-promoting factors (e.g., the synthesis and secretion of interleukins), and the induction of disease in animal models (e.g., meningitis, sepsis, gastrointestinal infections, acute lung injury, and other inflammatory reactions).
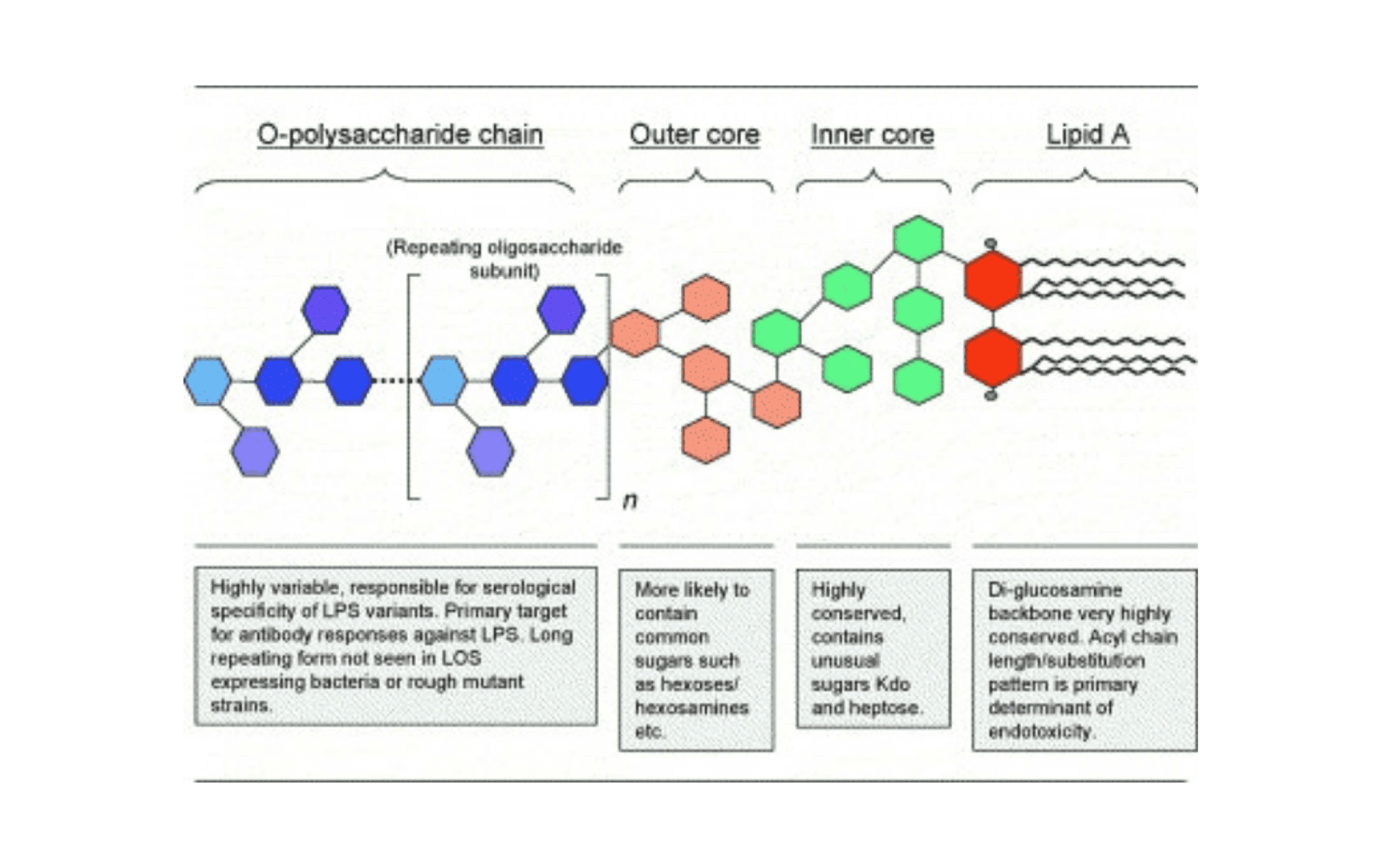
Molecular Structure
LPS is composed of three main components: lipid A, core oligosaccharide, and O side-chain.
Lipid A, composed of two glucosamine units, phosphate groups, and multiple fatty acids, serves as the bioactive center of LPS and is a major component of bacterial endotoxins. The structure of lipid A is highly conserved within the same bacterial species.
O side-chain, also known as the O-antigen, determines the bacterial serotype and is highly variable among different strains of bacteria. It protects bacteria from the harmful effects of antibiotics and provides resistance against the lytic action of the complement system. O side-chains are polymers of varying degrees of polymerization consisting of interconnected oligosaccharides of a certain lengths. They are structurally unstable.
An essential round-up of science news, opinion and analysis, delivered to your inbox every weekday.

Copyright © 2015-2024 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.